Hemolytic disease of newborn
Under hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn understand hemolytic anemia, which occurs due to antigenic differences of maternal and fetal erythrocytes (newborn), generation of immunocompetent System maternal antibodies against the antigen, penetration of antibodies through the placenta and the destruction of red blood cells of the fetus or newborn affected by these antibodies. The most common antibodies are directed against antigens of the rhesus, against the D antigen in the baby rezuspolozhitelnogo; They are produced in a woman rezusotritsatelnoy. Less antibodies directed against the group A or B antigens of the fetus (newborn); produced by her mother with a group O. Even rarer antibodies directed against antigens C, c, IS.
The etiology and pathogenesis of hemolytic disease of the newborn
The development of hemolytic disease of the newborn is most often associated with the incompatibility of blood between mother and fetus antigen D, at least - for the antigens of ABO, C et al.
Hemolytic disease, due rezusnesovmestimostyu, It develops as a result of penetration of the antibodies the mother through the placenta. These antibodies are fixed on the surface of the fetal erythrocytes, whereby the red blood cells are destroyed by macrophages. Developing hemolytic anemia with the appearance of pockets of extra-medullary hematopoiesis and an increase in the number of indirect bilirubin, highly toxic to the fetus or newborn.
Immunizing the mother Rh-positive red blood cells of the fetus during labor is carried out. Much less a woman immunized before pregnancy. The reason for this often is transfused erythrocytes antigen, Women's lack of. Chance of immunization of women is much higher in the case, if the husband and wife have the same blood group ABO system.
According to some reports, the likelihood of Rh-immunization at the same blood group of his wife and the husband at the penetration of the placenta 0,1 ml of fetal blood is not more 3 %, 0,25- 1 ml - 25 %, more 5 ml - 65 %. These data were obtained by the method Kleyhauera, which makes it possible to distinguish in the circulating blood of women fetal red blood cells in their content of fetal hemoglobin. According to poll results, the majority of women giving birth (75 %) penetrates no more 0,1 ml of fetal blood, which is not enough to immunize. In 3 % Women gets up 15 ml of fetal blood.
The total risk Rh immunization in the case, if the child is Rh-positive, Rh-negative mother and blood group ABO system, they are not the same, 2-3 %, and the coincidence of blood groups - 15%. This is due to the fact, that erythrocytes child, getting into the mother's blood in the same group, remain unchanged and it is not immunized, whereas fetal red blood cells are agglutinated a group of ABO agglutinins natural mother before, how they manage to immunize a woman.
Hemolytic disease of newborn - Term, It is often used as a synonym of anemia, associated with Rh incompatibility, however, it also includes other forms of hemolytic anemia, in particular hemolytic anemia, incompatibility of ABO system. Incompatibility system ABO is observed approximately 20 % all pregnancies. Only a 10 % pregnant women in the incompatibility groups ABO antibodies the mother affect the fetus.
Hemolytic disease THEY in children, mothers who have blood group O. Normal idioagglutinin ABO belong to the class IgM. They did not cross the placenta. However, 10 % healthy individuals with blood group O have antibodies against antigens A and B, belonging to the class IgG. Such antibodies are found in women, and men. They cross the placenta and can cause the fetus or newborn hemolytic anemia. ABO hemolytic anemia occurs among firstborn children as often, as for children, born from the second and third births. The frequency of hemolytic disease of the newborn increases with each successive birth.
The clinical manifestations of hemolytic disease
The clinical manifestations of hemolytic disease vary depending on the amount of antibodies, penetrated through the placenta. In the most severe cases, the fetus developed extensive edema, ascites, It appears in the pleural cavity transudate. A child may be born dead or in critical condition. In less severe forms of the disease in newborn pale skin, enlarged liver and spleen.
One of the most dangerous symptoms of hemolytic disease of the newborn is kernicterus, where there are signs of damage to the nervous system, leading eventually to irreversible changes - hearing loss, asymmetric spasticity. The critical level of indirect bilirubin, in which developing kernicterus, sostavljaet 307,8-342 mmol / l.
When the system ABO incompatibility clinical signs of the disease is much less pronounced, than with Rh incompatibility. Occasionally there is a significant increase in liver and spleen. Less severe degree of anemia, giperʙiliruʙinemii. Kernicterus is not characteristic of hemolytic disease ABO, However, isolated cases described her at this anemia.
Laboratory indicators of hemolytic disease
Blood picture depends on the severity of the disease.
In severe forms of the disease hemoglobin at birth is reduced to 3,72-4,96 mmol / l (60-80 G / l). Characteristically increase of reticulocytes 10-15 %, of leukocytes in peripheral blood, a large number of erythrokaryocytes, neutrophilic shift to the left.
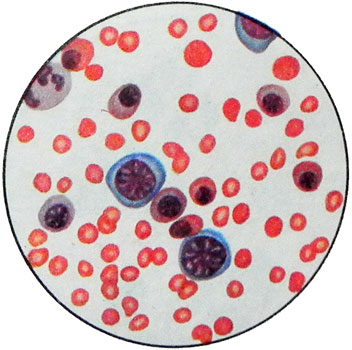
There are three degrees of severity of hemolytic disease of the newborn, depending on the blood levels of hemoglobin and bilirubin and the severity of edema:
- For I severity characterized by a hemoglobin 9,3 mmol / l (150 g / l), bilirubin less 90 mmol / l and subcutaneous tissue pastoznost;
- For the II degree - hemoglobin content 6,21- 9,31 mmol / l (100-150 G / l), bylyrubyna- 91-150 mmol / l, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue and ascites;
- for the III degree - the amount of hemoglobin less 6,21 mmol / l (100 g / l), bilirubin more 150 mmol / l, universal availability of edema.
Gradually, hemoglobin decreased, sometimes up to 1,86-2,48 mmol / l (30-40 G / l), the expressed eritrokariotsitoz, sometimes appear megaloblasts. In rare cases, the cells identified, very reminiscent of blasts. Found marked anisocytosis, polihromaziya. For Rh incompatibility characterized spherocytes. In the most severe cases, reduced platelet count.
When the system ABO incompatibility anemia is much less pronounced, than with Rh incompatibility. The level of reticulocytes also upgraded. In peripheral blood found erythrokaryocytes, but a small amount of (5-10 To 100leykotsitov). For this form of anemia characterized by the appearance spherocytes, which are indistinguishable from spherocytes in hereditary microspherocytosis.
Diagnosis of hemolytic disease of the newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn is expected in case of a birth in repeated births have Rh-negative mother's Rh-positive baby.
The content of hemoglobin in infants below the norm, jaundice with a high content of indirect bilirubin. Red blood cells contain antibodies child, detected by direct Coombs. Maternal serum contains antibodies incomplete, which appear during indirect Coombs test with a pool of donor Rh-positive red blood cells of the same group or the group O.
In cases, If Rhesus affiliation of the child and the mother or the child is the same Rh negative, maternal blood group O, and the child A, B or AB, and there are signs of hemolytic anemia, there is an assumption about the possibility of the system ABO incompatibility. This is supported by the detection of a maternal serum antibodies against antigens A or B (depending on the child's blood group), belonging to the class IgG.
The used test for the presence of the so-called immune idioagglutinin, giving hemolysis at 37 ° C prisutstvii complement, not characterize antibodies, causing hemolytic disease of the newborn, incompatibility of ABO system. The destruction of the red blood cells of the child is not due to their complementdependent hemolysis, as a result of destruction of red blood cells by macrophages, coated with IgG antibodies. Therefore, modern research methods are based on the destruction of IgM antibodies mercaptoethanol or 2,3-Dimercaprol (unithiol) followed by determination of serum antibodies or by indirect Coombs, or during incubation with gelatin solution. However, this method needs to be tested, because you can not completely exclude the possibility of fixing the wreckage IgM to red blood cells and to identify their indirect Coombs test, or by incubation with a solution of gelatin. Therefore, the development of new methods for the detection of antibodies, causing hemolytic anemia, when incompatibility ABO system.
Antenatal diagnosis of hemolytic disease of the newborn, associated with Rh incompatibility, It carried out primarily by dynamic studies of antibodies against the Rh antigen in the mother's serum. The increase in antibody titer during pregnancy suggests the possibility of Rh incompatibility in the fetus.
For antenatal diagnosis is also used transabdominal amniocentesis. According to researchers, it should be carried out only after the ultrasound examination to determine the location of the placenta. Although in most cases, transabdominal amniocentesis - Security Procedures, described in the literature as a complication of the mother (amniotic fluid embolism), and from the fetus (cardiac tamponade resulting hemopericardium). Dynamic study of amniotic fluid allows 93,3 % antenatal cases the correct diagnosis of hemolytic disease, to determine its severity and the prognosis for the fetus.
For antenatal diagnosis is important dynamic studies of bilirubin, which thus increases.
