Physiological characteristics colpocytologic pictures at different ages
According to some researchers, in the first days of postnatal period in girls is observed a slight increase in the excretion of estrogen - the result of hormonal balance, the fruit from the mother. During a few days the mother hormones excreted from the body of the child, and thereafter, before puberty, urinary estrogen remains low. Thus, gonads girls before puberty are in a state of relative calm.
Cytological smears of the vagina content newborns resemble smears of women in the luteal phase of the normal menstrual cycle. In the first days after birth is dominated by surface cells, sometimes with pyknotic nuclei. Gradually the surface cells and disappear after 2-3 weeks after the birth of infants in the vaginal smears appear and begin to dominate the intermediate and parabasal cells. Such a composition of a smear can be observed before puberty.
The reproductive period
In reproductive periods ovarian cyclical changes occur, characterized by periodic appearance of uterine bleeding (menstrual cycle). There are three phases:
- menses;
- postmenstrual, or proliferative;
- premenstrual, or secretory.
Since in the proliferative phase the ripening ovarian follicle primary, then it is also called follicular, and luteal predmenstrualnuyu- (it is in this phase in developing ovaries and corpus luteum produces progesterone).
On the basis of calculation in a smear of epithelial cells and non-epithelial elements can give an accurate description of all phases of the menstrual cycle.
Averages cellular composition of vaginal smears during the normal menstrual cycle | ||||
The phase of the menstrual cycle | The phase of the cycle | Cells strokes, % | ||
| surface | intermediates | parabasal | ||
| Menstruation | 1 | 17,2 | 73,6 | 9,2 |
| 2 | 12,5 | 72,7 | 12,8 | |
| 3 | 12,5 | 76,2 | 11,3 | |
| Early follicular | 4 | 27,2 | 70,5 | 2,3 |
| 5 | 43,9 | 54,3 | 0,8 | |
| 6 | 60 | 39,7 | 0,3 | |
| Average follicular | 7 | 74,4 | 25,6 | 0 |
| 8 | 81,2 | 18,8 | 0 | |
| 9 | 83,7 | 16,3 | 0 | |
| 10 | 86 | 14 | 0 | |
| Late follicular | 11 | 88,5 | 11,5 | 0 |
| 12 | 92 | 8 | 0 | |
| 13 | 94,6 | 5,4 | 0 | |
| 14 | 96,5 | 3,5 | 0 | |
| Early luteal | 15 | 90,9 | 9,1 | 0 |
| 16 | 79,4 | 20,6 | 0 | |
| 17 | 67,8 | 32,2 | 0 | |
| 18 | 62,2 | 37,8 | 0 | |
| The average luteal | 19 | 56,7 | 43,3 | 0 |
| 20 | 43 | 57 | 0 | |
| 21 | 33,8 | 66,2 | 0 | |
| 22 | 16,2 | 83,8 | 0 | |
| 23 | 9,7 | 90,2 | 0 | |
| 24 | 18,7 | 81,3 | 0 | |
| Late luteal | 25 | 12,6 | 87,4 | 0 |
| 26 | 6 | 94 | 0 | |
| 27 | 4,4 | 95,5 | 0,1 | |
| 28 | 3,9 | 94,7 | 1,4 | |
During menstruation there is a significant rejection of the cells of the vaginal mucosa, and therefore smears found in almost all kinds of vaginal epithelial cells, a significant number of erythrocytes and leukocytes, as well as large amounts of mucus.
Follikulinovaya phase
There are early, middle and late follicular phase.
Early follicular phase (4-7 Th day cycle) characterized by a predominance of intermediate cells in smears with clear contours, painted in green- blue tone (basophil). Can meet single parabasal cells. The cytoplasm of the superficial cells predominantly basophilic, therefore indicators of EI and CI low (EI - here 1 to 20 %; KI - from 1 to 30 %). The cells are arranged in groups, Translucent background smear because of muddy slime, a moderate number of leukocytes, can meet the red blood cells and histiocytes; Sometimes there is a small amount of sticks Dederleyna.
Average follicular phase (8-11 Minutes Cycle days) characterized by a decrease in the number of intermediate and increase of the number of superficial cells. The number of eosinophilic granulocytes and cariopyknotic superficial cells (EI - here 20 to 50 %; KI - from 30 to 50%)- The cells are arranged separately, background smear considerably enlightened. The number of rods Dederleyna, almost disappear leukocytes.
The late follicular phase (12-15 Th days of the cycle) It is characterized by an increase in the number of mature surface cells, arranged separately in the form of thin flat transparent plates. By the end of the late follicular phase of the surface cells are characterized by pronounced eosinophilia and painted mainly in bright colors. Dimensions cells reach their maximum value, their nuclei undergo pyknosis.
A typical feature of the late follicular phase of the cycle is the isolated cell placement at a certain distance from each other and their arrangement in the form of tiles, When the contours of a single cell is easily visible through the transparent cytoplasm other.
There bright transparent background smear in the absence of leukocytes and the presence of sticks Dederleyna. EI and CI at the end of this phase, also called preovulatory, peak (EI - here 50 to 70%; KI -from 50 to 80 %). Reduced proliferation after 14-15-day cycle is an indicator of ovulation occurred on the eve of.
Lyuteinovaya phase
IN early luteal phase (16-18 Th days of the cycle) there are signs of the influence of progesterone in the form of tightening margins flat surface cells. Gradually the number of superficial cells begins to decrease, and intermediate - to increase. EI and CI 60-50 to ponyzhayutsya %. Due to the changing nature of mucus smear leukocytes and the appearance becomes turbid, dusky.
The average luteal phase (19-23 Minutes Cycle days) characterized by increasing the number of intermediate cells and a decrease in the number of surface. Cells predominantly basophilic (therefore the EI and CI 23 day cycle significantly decreases), form a group (4-6) or congestion.
Late luteal phase (24-28 Th days of the cycle) characterized by massive desquamation of epithelial cells, caused by the influence of progesterone. Dominated by intensely colored intermediate basophilic cells, arranged in groups and formations. The value of intermediate and superficial cells decreases.
By 27-28 th days of the cycle in smears found a solid formation of intermediate cells without precise contours on a dark, dirty background, conditioned detritus and leukocytes. On the 26th day of the cycle has been a slight increase in EI and CI (second peak), then before menstruation values of these parameters decrease sharply.
Thus, increasing estrogenic stimulation follicular phase of the cycle causes the intense proliferation of the vaginal epithelium, and alternating progesterone effects - enhanced epithelial desquamation and cell transformation characteristic. The study of these changes gives some idea of the ovarian activity in normal, and in pathological conditions.
The indices of ripening, karyopyknosis and eosinophils in the normal menstrual cycle | |||||
| Phase of the cycle | Maturation index, % | Index karyopyknosis, % | Index eosinophilia, % | ||
| Parabasal cells | Intermediate cells | Superficial cells | |||
| Early follicular | 1-3 | 80±7,9 | 20±2,4 | 15±2,1 | 10±1,9 |
<68-79> | <12-27> | <10-18> | <6-15> | ||
| Average follicular | 0 | 60-4-6,7 | 40±4,1 | 30±3,6 | 25+4,0 |
<43-72> | <31-50> | <21-40> | <15-30> | ||
| Late follicular | 0 | 15+2,1 | 85±9,3 | 80±9,3 | 75-6.0 |
<5-18> | <70-95> | <62-90> | <60-80> | ||
| Early luteal | 0 | 60±6,2 | 40±5,3 | 303,9 | 25±4,7 |
<49-70> | <31-50> | <24-39> | <17-34> | ||
| The average luteal phase | 0 | 80±9,3 | 20±2,9 | 10±2,0 | 8±1,9 |
<68-90> | <9-28> | <8-18> | <4-12> | ||
| Late luteal | 0 | 90±6,8 | 10±2,7 | 5±1,4 | 4±1,1 |
<80-96> | <5-12> | <2-3> | <2-7> | ||
Cytological changes in the vagina It can be used to determine the date of ovulation. To do this, you must carry out cytology dynamics, from him for a few days before the expected date of ovulation and ending a few days after her. At the time of ovulation in a smear dominated mature cells of the surface layer of polygonal shape with eosinophilic cytoplasm and pyknotic nuclei.
Location cell separation, Smear a light background, clear. At the time of ovulation EI and CI reach its maximum value. Besides, preovulyarnogo to smear characterized sticks Dederleyna and lack of white blood cells. In the study of smear after 4-5 days after ovulation observed decrease in CI and EI, the appearance of folding, clustering of cells, the location of their groups and layers.
A similar pattern of changes in the cytological picture of vaginal smears, is to shift from a maximum differentiation and proliferation of cells to transformation luteal, It noted only under the influence of sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone), produced mature follicles, and then the corpus luteum of the ovaries. Therefore, changes in the vaginal mucosa can be used as a diagnostic test for evaluation of ovarian function.
Symptom crystallization mucus of the cervical canal – Symptom fern
If the slide strip applied mucus endocervical, taken from normally menstruating female midcycle, after drying at a small increase in smear microscopy is clearly visible pattern, resembling fern - arborizacii the phenomenon of Papanicolaou. It is believed, crystals, formed in the mucus of the cervical canal, It consists of sodium chloride. There are large crystals in the form of fern leaf (+++), smaller and thinner (++), naked skeletizirovannye, like leaves with dangling (+). No crystals represent minus (-).
In the normal menstrual cycle, the crystallization occurs on days 7-8, then during the follicular phase of the cycle, its intensity increases. In the late follicular phase, Ovulation occurs on the eve of the maximum intensity of mucus crystallization (+++), that is the highest rise of EI and CI.
At the beginning of the luteal phase of the cycle fern as it loses its ramifications, and in the late luteal crystallization completely disappears. According to some authors, the degree of crystallization of mucus is directly proportional to estrogenic activity. To determine the activity of progesterone it is almost irrelevant. The phenomenon of mucus crystallization is used to determine the hormonal ovarian function.
Menopause
Menopause characterized by a complex rearrangement of functions of the endocrine glands, particularly ovarian. Changes, occurring in the ovaries, cause irregular menstruation or a metrorrhagia. Menopause is usually established after several years of menstrual disorders, less - immediately after menstrual cycles, which can have both ovulatory, and anovulatory character.
Termination of ovarian cyclic activity It leads to a cessation of cyclical changes in the mucous membrane of the vagina. However, its proliferative changes are expressed for a long time, despite the onset of menopause. During, predšestvuûŝij menopause, often disappear cyclic changes of the mucous membrane of the vagina, not observed peaks of EI and CI during ovulation, no luteal conversion, characteristic of the functioning of the corpus luteum.
Type of strokes, svojstvennyj klimakteričeskomu period, it is impossible to allocate. Pathological manifestations of menopause should include as persistent high degree of proliferation, and pronounced atrophic changes.
Menopause
In the first months, and sometimes years of menopause vaginal smears different persistence patterns and often remind one of the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle. The first two years of menopause are characterized by high estrogen excretion, after which it was reduced by almost half, remains at this level for a long time.
There are several types of vaginal smears, characteristic of menopause.
Smears proliferative type
The predominant cells of the surface layer, which may be located separately; CI and EI is still quite high. Leukocytes in a small amount or absent, almost always found sticks Dederleyna, Smear a light background.
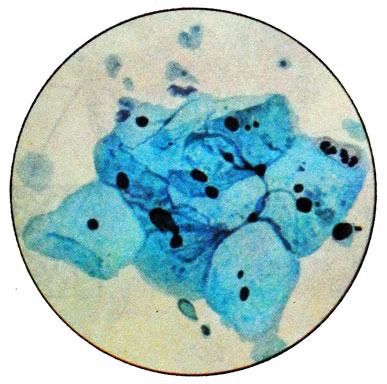
Such strokes occur in 26 % Women in the first five years of menopause and reflect a lack of progesterone in the ongoing activity of the ovaries production of estrogen.
Smears intermediate type
Intermediate cells predominate (to 90%), which are arranged in groups, layers and separately. Twist the edges of the cells (as in the progesterone stimulation) not observed. There are a small number of surface cells, predominantly basophilic. THAT 15%; EI - up 10%. The index of maturation absent or greatly reduced - 0/100/0; 0/90/10; 0/85/ /15. Observed in 37 % women 3-5 years after menopause.
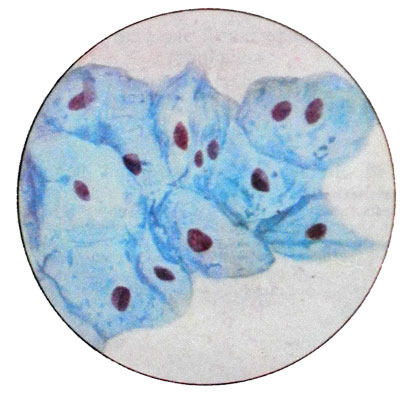
Smears of mixed type
Smears of mixed type are characterized by different amounts of surface, intermediate and parabasal cells.
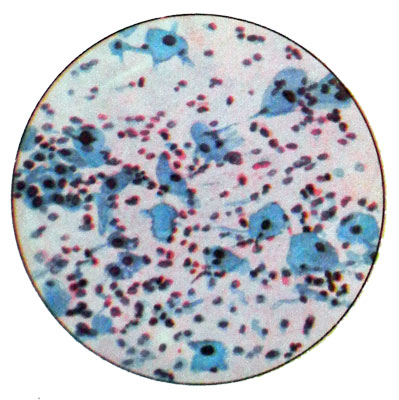
The number of leukocytes is impermanent: a lot of them, or they are completely absent. Sticks Dederleyna often not detected. Swabs of this type are transitional to the true and observed in atrophic menopausal 12 % Women.
Smears of atrophic type
Basically they found parabasal cells.
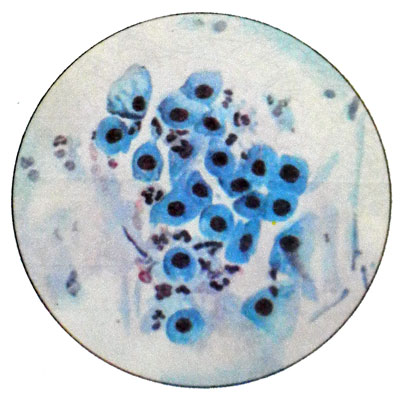
When mild atrophy occur intermediate cells (to 50%). The emergence of parabasal cells of the lower layers shows a deep atrophy of the vaginal mucosa. Leukocytes in large quantities, Sticks Dederleyna missing. This type of smear is observed after five years from the onset of menopause (in 17 % Women) and evidence of sharply reduced production of estrogen by the ovaries.
Smears cytolytic type
Against the background of the detritus from the scraps of the cytoplasm and separately lying bare nuclei of cells destroyed a large number of sticks Dederleyna, contributed cytolysis intermediate cells. Superficial cells more resistant and did not undergo cytolysis.
Smears androgenic type
Common in women after removal of the ovaries during menopause. In this light strokes, with a transparent background. Identified intermediate cells with basophilic cytoplasm, leukocytes are absent. Coli can be detected Dederleyna.
The appearance of five years or more from the start of menopause smears of proliferative type, in which the number of surface cells exceeds physiological norm, It may be associated with a pathological process in ovarian and breast cancers.
