Fiʙrinoliz – The system of hemostasis
The enzyme system, causing asymmetric splitting of fibrin / fibrinogen into smaller and smaller fragments, called fibrinolytic, or plasmin.
The main component of this system It is enzyme plasmin (fiʙrinolizin), contained in the blood plasma as zymogens (plasminogen) in an amount of about 0,2 g / l.
The blood circulating plasminogen occurs in two major forms:
- in the form of native zymogen with NH2-terminal glutamic acid - deaf–plasminogen;
- in the form of a partially exposed to proteolysis lys-plasminogen, which is 10-20 times faster, Cem Glu-plasminogen, is transformed into plasmin physiological activators, It has a much higher affinity for fibrin and is quickly metabolized, Cem Glu-plasminogen (half-life in the blood is suitably 0,8 and 1,24 Nights).
Active plasmin quickly locked antiplasmin and eliminated from the bloodstream. As a result, after the introduction of streptokinase or urokinase plasminogen levels in the blood very quickly and strongly reduced (for large therapeutic doses to almost zero), and then, If it terminated its further activation, for 18-28 hours restored. This ability of plasminogen activators quickly deplete stocks specified proenzyme must be considered in the treatment of thrombosis.
Activation of fibrinolysis body, as well as activation of blood coagulation, It can be carried out both on the outside, and the internal mechanism.
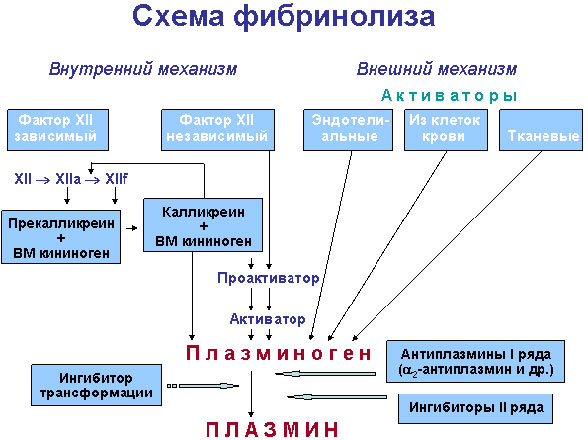
The internal mechanism It may be triggered by the same factors, that blood coagulation, t. it is. complex XIIa or kallikrein with XIIf and high kininogenom. The activity of this mechanism will be assessed at the rate of lysis fraction euglobulin, prepared from the blood, pre-activated terminal (kaolin). Along with this factor-XIIa-dependent lysis there is some mechanism internal activation (about equal in strength), stimulants which are not yet defined.
External activation of fibrinolysis is mainly synthesized in the vascular endothelium, the so-called tissue-type activator protein (Bridging Digital Divide). Identical or very similar with him are many activators tissues and body fluids, but endothelial most easily enters the bloodstream. Turbo it occurs when all kinds of vascular occlusion, including compressive vascular cuff (manzhetochnaja is based on the sample), in various physical activities, under the influence of vasoactive substances and medicines — Nicotinic Acid, Adrenaline and noradrenaline, vasopressin analogues and others.
Powerful plasminogen activators are also contained in blood cells is the erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes. Besides, granulocytes and macrophages can secrete intracellular kinases, which in themselves, t. it is. without the participation of plasmin, break down fibrin.
Plasminogen activators are also contained in various tissues and secrets and jekskretah-urine, milk, bile, saliva, etc. Most of these activators is identical to sosudistomu jendotelial'nomu. A very large number of activator and some cells produce tumors (melanoma).
Urokynaza, jukstglomeruljarnom complex formed in the kidneys and in most released in the urine, different from other solvents. In the blood it gets in a little, Therefore, urokinaznaja is only about activation 15 % total plasma fibrinolytic activity. Urokinaza is widely used as a therapeutic drug in need receiving Thrombolysis. There are two known molecular forms this activator.
From alien activators fibrinolysis in therapies tromboamboliy often apply different kinds of streptokinase, at least-activators of fibrinolysis of other bacteria and fungi.
Fibrinolysis is inhibited in antiplazminami, the most important of which is specific to α2-globulins (molecular weight: 65000-75000) Quick doesn t, contained in the plasma in the number 0,07 g/l and can neutralize approximately 2/3 total plasmin, from full activation plazminoguena blood. Equally important is the role of the newly opened high-speed antiaktivator, inhibits fibrinolysis Activator tissue type (endothelial plasminogen activator).
Among the inhibitors of fibrinolysis, with a weak effect, merit α2-makrohlobulyn, C1-jesteraznyj inhibitor, antitrypsin and others.
Alpha2-makrohlobulyn, connecting with plazminom, protects the last from the more powerful inhibitor α2-antiplazmina and at the same time prevents the action of plasmin on Fibrinogen, t. it is. orients the proteoliticeski enzyme on lysis of fibrin.
Plazminovaja system adapted to lizisu fibrina in sgustkah (report) and soluble fibrin-monomeric complexes (RFMK), therefore Fibrinogen Lysis and other plazminovyj proteins (factors V and VIII) occurs only with very strong its activity (eg, intravenous streptokinase or urokinase). This is facilitated by a number of mechanisms, the most important of which is linking woven Activator, Liz-plasminogen and plasmin fibrin, Thus the report creates a high concentration of components of fibrinolytic system, and then, that these fixed on report components loosely Ying- gibirujutsja antiaktivatorami and anti- plazminom, While freely circulating plasmin and its vascular Activator form with their bad inhibitors dissociirujushhie complexes.
Due to the action of inhibitors of normal blood clots, obtained as a result of its natural collapse in test tubes, exposed under normal conditions of very weak lizisu, the most affordable way to determine which is the a study of a natural clot Lysis on m. A. Kotovshhikovoj and b. AND. Kuzniku or this same test in modification (e). P. Ivanova.
In contrast,, jeuglobulinovyj Lysis (Kovalsky method or Kovarzhika) occurs quickly enough and full of, because the allocation of jeuglobulinovoj plasminogen activators and his faction of the precipitate, Whereas inhibitors of fibrinolysis (doesn t, antiaktivator) remain in the bulk of the supernatant and are not involved in the reaction. Thus, in the study of fibrinolysis inhibitors Lysis jeuglobulinovogo artificially removed from the reaction mixture and practically only determined the activity of plasmin and its activators. By virtue of this the weakening of the (slowdown) jeuglobulinovogo Lysis talking about reduced content in researched plasma tissue Activator type (endothelial) or plasminogen, and acceleration — increased content Activator when sufficient quantities of plasminogen.
Jeuglobulinovyj Lysis is determined also internal XIIa-dependent activation of the fibrinolytic system. So preinkubacija blood with kaolin, the calling intensive contact activation of factor XII, prekallikrein, and high molecular weight kininogen (in the complex), reduces the time jeuglobulinovogo Lysis with 2-4 hours to minutes.
Active plasmin induces consistent asymmetric cleavage Fibrinogen/fibrin.
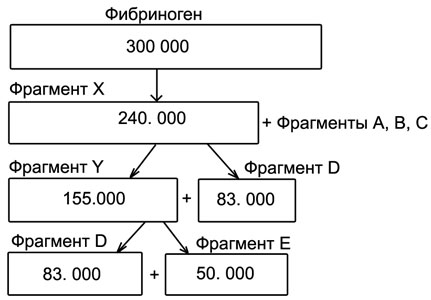
At the outset of its α- and β-chains of tiny molecular fragments, total mass is about 40000 Dalton. After chipping them in plasma remains large molecular fragment X, which yet retains the ability to form fibrin (curdle) under the influence of Thrombin. Then as a result of plasmin X fragment cleaved into fragments Y and D, a fragment of the Y is in fragments (D) and (E). Krupnomolekuljarnye products of fibrinolysis (fragments X and V) referred to earlier (they, as soluble fibrin-monomeric complexes — RFMK, are defined using bonding tests Staphylococcus, LaTeX-aggljutinacionnym test), and fragments of D and E — late, or end. The latter often identifies (especially when fibrinolize, not fibrinogenolize) in the form of D-Dimer D or D-trimerov D-E.
Later products of fibrinolysis immunologically detected using specific serum antifibrinogenovyh (in this case, you define a sum of products fibrinolysis I RFMK, If the latter has not been removed) using specific Antisera, or poison snakes EFA. Normal serum fibrinolysis products (PDF) less 0,05 g / l (to exclude secondary fibrinolysis in vitro blood taken from a vein, adding to it immediately aminokapronovuju acid).
Increased blood PDF shows about what is happening in her active fibrinolize.
Primary increased fibrinolytic activity (without prior blood clotting) — extremely rare. It is registered in a few cases of hereditary deficiency of α2-antiplazmina, and from molds — melanoma, to produce a large amount of tissue-type plasminogen activator. It is also envisaged the possibility of activation of fibrinolysis coagulation without prior in severe liver problems as a result of reduced synthesis of α in it2-antiplazmina. But, because with such develops lesions, usually, DIC, the specified activation of fibrinolysis in the vast majority of cases, you should communicate with the preliminary liquidation of blood.
Thus, activation of fibrinolysis without prior blood clotting-casuistry, If you do not take the artificial activation through the use of streptokinase and its derivatives, urokinase, fast tissue Activator type (in recent years comes as drug therapy) and other drugs. In the vast majority of similar clinical situations fibrinolysis is secondary and associated with disseminated intravascular blood collapsing, either with massive trombojembolijami, as well as with intense local gemokoaguljaciej in or angiomah. Therefore increasing the level of PDF is regarded as an indicator of intravascular clotting, and the secondary activation of fibrinolysis.
Increasing the level of PDF when DIC-syndrome and massive thrombosis very often combined with slowing jeuglobulinovogo and XIIa-dependent fibrinolysis, with the decline of plasminogen in the blood. There is no contradiction, for fibrinolysis PDF education occurs in the report and mikrosgustkah fibrin, where fixed plasminogen and its Activator, intensely formed and rapidly metabolized active plasmin. Lysis in report and sgustkah leads to admission into the bloodstream of large quantities of PDF, but due to attrition in plazminoguena blood clots and its past number of activator in circulating blood and plasma naturally decreases.
Thus, increasing the level of PDF in combination with decreased content of plasma plasminogen activator and it is legitimate signs of intense intravascular clotting. Antiplazminovaja activity may increase as, and remain normal or moderately decrease.
The second manifestation of intravascular clotting in the blood circulation is a complex of plasmin-doesn t (as the complex Thrombin-Antithrombin). The formation of these complexes with inhibitors activated enzymes is accompanied by the emergence of new antigenic markers, that do not exist separately in enzymes (plasmin, Thrombin) and their initial. The identification of these neoantigenov is used in the diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome and other kinds of intravascular clotting.
Products, formed as a result of fibrinolysis, are biologically active and have an effect on permeability and vascular tone, properties of the endothelium, inhibit platelet aggregation and fibrin monomers self-assemble (t. it is. act as antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants), inhibit fibrinolysis, have an activating effect on the system of mononuclear phagocytes, absorbed by the system and block it, interact with the complement system and so. d.
