Microscopic examination of urine: elements of organized urine sediment
Red blood cells in the urine
The first morning urine is not normal red blood cells, but may meet individual unmodified copies, trapped in the urine as a result of scratching itch of external genitals,due to injury of the urinary tract or in salt crystals from the vagina in women before- and postmenstrual period.
The diseased urine red blood cells can be found in varying amounts. The presence of erythrocytes in urine (hematuria) evidence of bleeding in the urogenital system. There are gross hematuria, when urine has a significant admixture of blood and discolouration (reddish or brownish), and microhematuria, characterized by a small number of red blood cells, identified only microscopically (the color of urine is not changed).
Depending on the reaction of urine and its concentration, as well as the length of stay of red blood cells in urine color and shape of their changes.
In weakly acidic urine red blood cells They remain unchanged for a long time and have a kind of circular discs yellowish green color. When red blood cells swell due to the small relative density in a very weakly acidic or weakly alkaline medium they have a kind of delicate pale yellow or pink disc slightly larger, than normal erythrocytes.
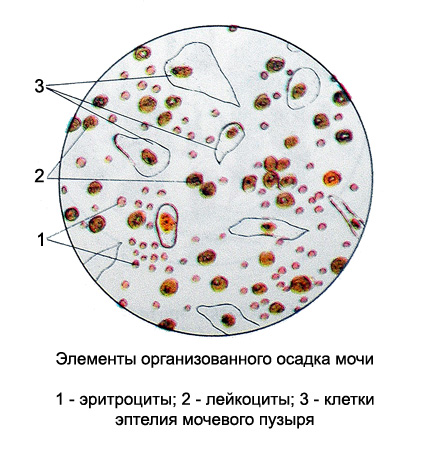
A more prolonged effect acidic urine red blood cells in the kidney contributes to their leaching (the loss of an alkaline substance hemoglobin), and therefore already in a fresh urine they have the form of rings of different size colorless. These RBCs may sometimes occur in the form of particles and cell debris, (fragmented erythrocytes). The appearance of the modified red blood cells in the urine (razbuhših, fragmented, leached) It must be marked in each case, since it is of great diagnostic value.
White blood cells in urine
Most often found in the urine neutrophilic granulocytes, which are slightly larger than red blood cells, round shape. Depending on the reaction and the concentration of urine, they have a different kind:
- in a weakly acid medium, eg, neutrophilic granulocytes usually grainy, round, Colorless, their core consists of several segments;
- in an acidic environment, they shrink and become glassy;
- tuberculosis may acquire gvozdevidnuyu (an elongated thickened at one end) form;
- in alkaline urine neutrophil granulocytes lose granularity and contours, swell and increase somewhat;
- rezkoschelochnoy in the urine, they are destroyed, forming a viscous, mucous sludge mass.
In some pathological conditions neutrophilic granulocytes may be subject to fatty degeneration. Swollen leukocytes, especially in the urine with a low concentration, significantly increased.
Separate neutrophilic granulocytes (to 10 in sight) found in the urine of any. Their appearance in a large amount of evidence of inflammation in the urinary organs, but does not indicate the site of inflammation. The localization of the inflammatory process detected on the basis of a general study of all sludge, by the presence of other formed elements (eg, epithelial) taking into account the clinical manifestations. Leukocytes are located separately, groups (Groups - close pile of white blood cells in several layers.) different size (from 15-20 to 100-200 of ½, ¼ and the whole field of view) and clusters (Clusters - lying next to cells, are easily account).
Eosinophilic granulocytes found in urine at a specific chronic pyelonephritis (tuberkuleznoho) and non-specific nature, as well as eosinophilic, t. it is. allergic, pyelonephritis and pielotsistite. Finding them in the urine sediment is important not only for diagnosis, but also for the treatment of patients with tactics.
Lymphocytes largest number of more red blood cells, Colorless, whitish, identify their cytoplasm in the form of native hard. Lymphocytes can be detected in the urine in the later stages of lymphocytic leukemia as a result of leukemic infiltration of the kidneys, and kidney diseases, the etiology of which is associated with immune factors (glomerulo- jade).
Epithelial cells in the urine
The urine sediment found in a healthy person is usually the individual epithelial cells of the bladder mucosa and flat epithelial cells of vaginal mucosa. Increased content of epithelial cells in inflammatory processes observed, and by the nature of the epithelium can determine the localization of the pathological process (mochetochnik, renal tubules, renal pelvis, and others.).
When pathological states sloughing of epithelial cells occurs under the influence of various agents (and other toxins.), which leads to changes in the physical and chemical state of the environment. Besides, urine, especially alkaline, also acts on cells separated, causing them to swell. All this suggests that the epithelial cells in the urine may be slightly different from the unmodified cells of normal. Practically epithelial cells in urine may be differentiated primarily on the basis of their forms and sizes taking into account various degenerative changes, presence of other elements (cylinders, amyloid cells of the prostate gland, grains and other lipids.), squirrel, Glucose, as well as the clinical data.
The epithelium of the mucous membrane of the vagina and external genitalia presented the broad, high, rounded, sometimes polygonal, sharply contoured, light, transparent and dimmer (in the state of keratinization) cells with one, centrally located nucleus; often in the form of bands or sheets. In larger or smaller number of flat epithelial cells found in the urine of healthy women. Grossly in the urine of women can detect small whitish flakes, consisting of layers of the stratum of the epithelium with clusters of various microorganisms from the external genitalia, as well as groups of flat epithelial cells, together with leukocytes, emanating from the vagina.
The epithelium of the urethra. The mucous membrane of the prostatic urethra in men covered with transitional epithelium, which goes into a cylindrical hole and at the outer - in flat. In normal epithelial mucosa of the urethra does not occur in the urine. In chronic urethritis in men, they have the form of flattened round form cells of medium size, light, often opaque, nezernistyh, whitish. The kernels are located in the center of, but poorly reviewed. There are individual instances, but most often cells form groups and clusters in the mucus together with leukocytes in urethral threads.
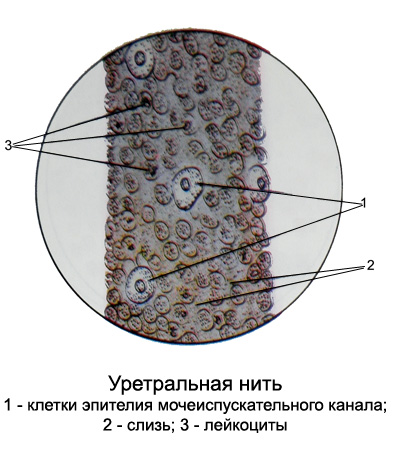
In women, the epithelial cells of the urethra flat, Similar to the cells of the vaginal mucosa, and therefore the investigation of urine of no note.
Urinary tract mucosa (Bladder, ureters, renal pelvis) vıstïlaet perexodnıy epithelium, form which varies depending on the degree of filling body. The transitional epithelium is referred to as a two-layer. It distinguish superficial and basal layers. The cell nuclei transitional epithelium vesicular, small size, and the cytoplasm is colored pigments in the urine slightly yellowish and contains grains.
The epithelium of the bladder in the urine sediment represented by large polygonal (sometimes rounded) flattened cells form the surface layer of the bladder mucosa with one, two or more fairly large vesicular nuclei, where much of the little shiny nucleolus.
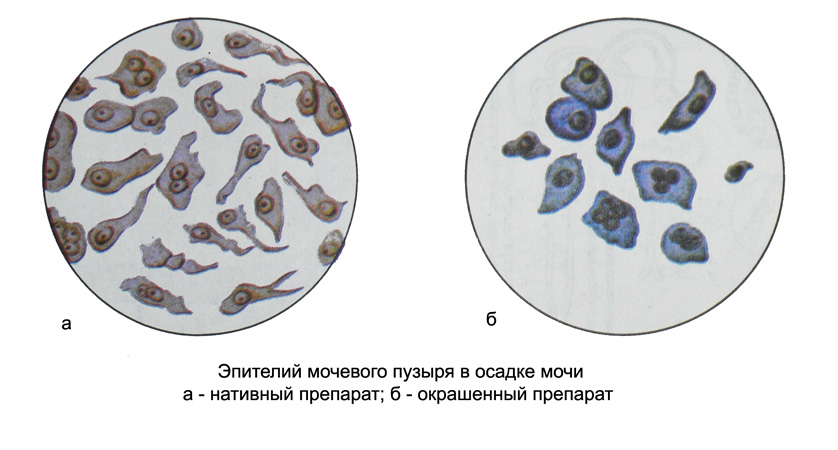
The cytoplasm yellowish detected grains of different sizes.
Along with these cells there are polymorphic cells of medium size, elongated or round (oval) shape, predominantly mononuclear, with fine grains in the cytoplasm (the top row of cells of the basal layer), as well as small spherical cells often (oval) shape, mononuclear, with fine grain size in the cytoplasm (bottom row of cells of the basal layer). Conventionally, the epithelium of the bladder is called superficial cells, intermediate and basal layers of mucosa.
Epithelial cells of the bladder may occur as isolated cells, groups and clusters.
Normally found in the urine sediment isolated epithelial cells. A large number of epithelial cells in the urinary bladder observed in acute catarrhal cystitis, as well as infectious diseases, or after ingestion of certain drugs (eg, geksametilentetramina, or hexamine). In chronic cystitis with a high content of epithelial cells of pus in the urine sediment slightly, it is sometimes difficult to detect even single cells. When pathological processes in the bladder epithelial cells may undergo fatty degeneration.
The epithelium of the renal pelvis and ureter. The cells of the epithelium slightly yellowish, different lengths, with a clearly visible nucleus and grit.
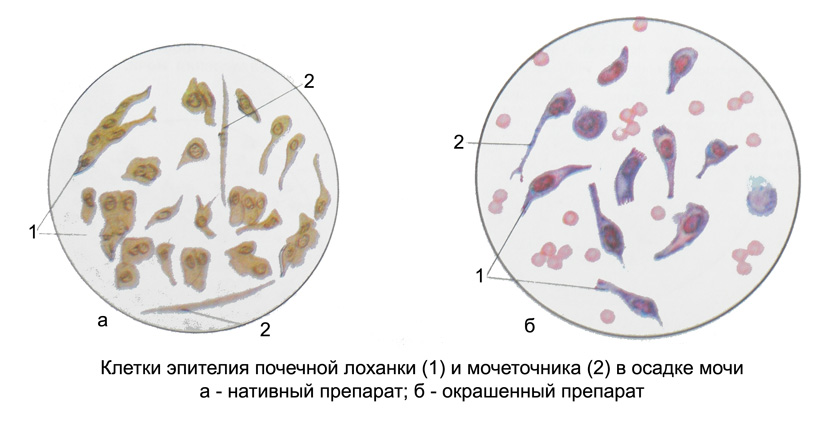
Epithelial cells of the renal pelvis may have tailed, spindle, pear shaped or oval, sometimes reminiscent of columnar epithelial cells, often located imbricate. These epithelial cells are found mostly in the catarrhal pyelitis. With the development of purulent pielita epithelial cells exposed to various dystrophic changes, mainly fatty degeneration. Because of the diverse forms of epithelial cells of the renal pelvis is often difficult to distinguish from the intermediate cells of the bladder. Therefore, when suspected pielit such epithelial cells marked with the epithelial cells of the bladder (cells of the mucous membrane of the urinary bladder and renal pelvis). Cells ureter transitional epithelium narrower, and sometimes considerably lengthened.
Award of epithelial tubule epithelium kwbïçeskïy nefronov. The urine epithelial cells that often irregular round (oval), less polygonal shape, with the core, reminiscent leached erythrocytes.

The cytoplasm of cells yellowish, with fine grains. Kidney epithelial cells readily undergo protein (grained) and fat (lipoid) distrofii, at which they become grainy or fat droplets, strongly refracting light. This small nucleus of the cell or completely unnoticed. When steatosis epithelial can significantly increase and reach the size of the cells of the intermediate layer of the bladder transitional epithelium. Chance of hyaline droplet degeneration and vacuolation. Kidney epithelial cells found in the urine in the form of individual cells, epithelial cylinders, in which cells are imbricate and unrelated clusters and groups. They often buropigmentirovany hemosiderin and yellowness painted in the presence of blood in the urine or bile pigments. Kidney epithelial cells found in the urine in acute and chronic kidney disease, along with kidney and protein cylinders.
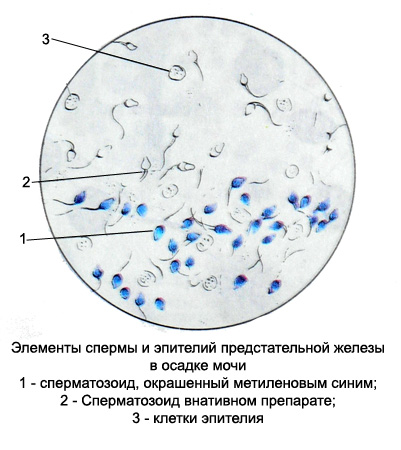
Prostatic epithelium. In cases impurities prostatic secretions to urine (especially in elderly and senile) epithelial cells are found in the sediment of the prostate. Normally, they are colorless or whitish, cylindrical shape, with big round or oval nucleus. In the pathology they look small round whitish fat cells drops (zhirovaya dystrophy). Unlike prostate epithelial cells from other cell, mainly from kidney epithelial cells, Similar to their size, It is, they occur in a protein-free urine or small quantities of protein (in trace) and the absence of renal cylinders. Besides, usually with the epithelial cells of the prostate gland and other elements found her secret (colloid mucus, grain lipids, amyloid corpuscles and often sperm).
The epithelium of the mucous membrane of the uterus It consists of a small cylindrical cell colorless, often in a state of fatty degeneration. The urine is found in the mucous or muco-purulent and bloody scraps, released from inflammatory diseases of the uterus, after aspiration of the liquid from its cavity or during menstruation and shortly thereafter.
Cylinders are casts of the tubules of nephrons cylindrical shape in the form of direct and convoluted structures of varying widths and lengths.
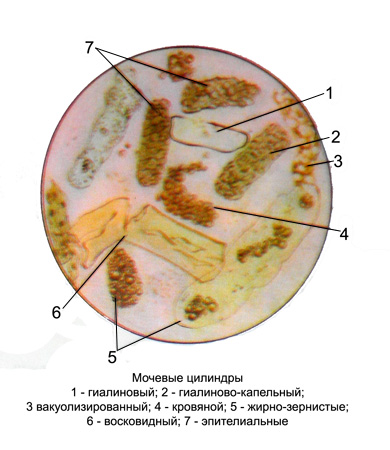
They have a uniform outline, rounded at one end, and the other end to them as broken off, interrupted. In acidic urine cylinders are kept intact for a long time, and alkaline rapidly destroyed. Kidney cylinders found in the urine almost always along with protein and renal epithelium. The presence of cylinders - the first sign of reaction to the total kidney infection, intoxication or for changes in the most kidney, therefore cylinders and epithelium are very important for the laboratory diagnosis of kidney disease. Cylinders easiest identified in the first morning urine.
Hyaline casts (belkovye slap kanalʹcev nephrons) - Direct and convoluted a homogenous structure, pale and almost transparent; length, width and shape of their various, at one end, they generally rounded, wider ones often have depressions. Observed in urine at all kidney, but their number is not dependent on the severity of the pathological process. In hemorrhagic nephritis cylinders painted in brownish or yellowish, and jaundiced urine they chartreuse.
Sometimes hyaline cylinders partially covered with amorphous urate and phosphate, kidney epithelial cells, erythrocytes and leukocytes. Hyaline casts can not see, especially if they are a little bit. It is easier to come to light in the investigation of these formations under low magnification with condenser or lowered significantly narrowed aperture.
Granular casts formed from granular degenerated epithelial cells of the kidney or granular masses of broken cells, is a protein particle. Granular casts are usually short and thick, sometimes with cross interceptions, in which they easily break, forming debris. Granular casts haemosiderin in stained reddish-brown or brown (buropigmentirovannye) and bile pigments in yellow. Hyaline casts, coated with amorphous salts, Unlike granular usually lighter, narrower and longer, They do not have a continuous grain (they can detect highlights, devoid of grain). Besides, These cylinders are not peculiar granular casts and impressions circuits, which correspond to the mutual fitting properly degenerative kidney epithelial cells. By adding one drop of 10 % acetic acid solution to dissolve the amorphous phosphates, and protein grains remain undissolved. Granular casts are found in all acute and chronic kidney disease.
Epithelial cylinders formed from epithelial tubules of nephrons. Sometimes kidney epithelial cells are deposited on the surface of hyaline cylinders. Epithelial cylinders appear in the urine for various renal diseases. Can be pigmented hemosiderin and bile pigments.
Buropigmentirovannye cylinders - Is granular and epithelial cylinders, pigmented haemosiderin. There glomerulonephritis.
Blood cylinders It consists of erythrocytes, often leached, cylindrical or blood clots, formed in the tubules of the nephron. There, as buropigmentirovannye, glomerulonephritis.
Leukocyte cylinders composed of white blood cells and are formed by purulent process in the kidney - pyelonephritis.
Fatty granular casts more or less densely covered with large or small droplets of fat, strongly refracts light; found in the urine of nephrotic form of chronic glomerulonephritis, lipoid nephrosis, etc..
Waxy cylinders much wider hyaline, It has a pale yellow color matte, Homogeneous, direct, extensive, clearly contoured. Often in these cylinders have slots (longitudinal and transversal cracks), therefore, they are broken down. Any deposits they discover rare. The appearance of waxy cylinders indicates severe kidney disease and, apparently, It is the result of a qualitative change in the protein (preamiloidoz or amyloidosis).
Hyaline droplets cylinders It consists of matte whitish hyaline drops (resemble in appearance a gray astrakhan) and are a consequence of its irreversible changes. Observed In advanced disease processes in the kidneys (chronic glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome).
Vacuolated cylinders - Is able to epithelial cylinders marked vacuolization. There are at severe renal impairment (especially in the form of chronic glomerulonephritis hematuric).
In severe glomerulonephritis with nephrotic component, as well as nephrotic syndrome in the urine sediment can be found hyaline droplets and hyaline balls and lumps (formation of a rounded or irregular shape), which means that the appearance of deformation and expansion of the tubules of nephrons.
From the cylinders should be distinguished цilindroidы, is a long ribbon-like formation of soft pale longitudinal depravity, consisting of mucus. They are much longer than hyaline casts, ends fringed, often split. Unlike cylinders cylindroid not dissolve in acetic acid and in alkaline urine. Цilindroidы, as cylinders, They may be coated with amorphous phosphate, that the addition of acetic acid to dissolve. In normal urine, there are individual cylindroid.
Fibrin in the form of fibrous scraps burookrashennyh detected in the urine for the second or third day after gross hematuria. In the urinary sediment can be found at the same leached and fragmented erythrocytes.
Elements of the sperm and the secretion of the prostate found in the urine as normal, and with genital diseases, various forms of spermatorrhea.
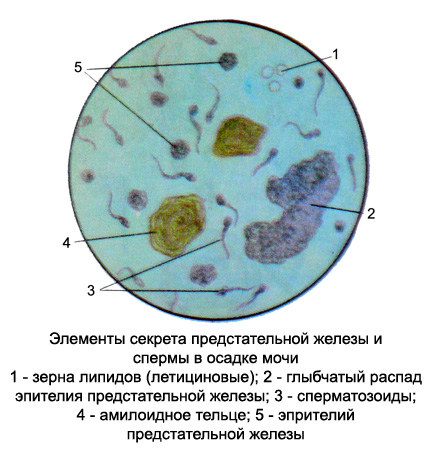
With the touch of prostate secretion in the urine can get amyloid (Layered) calf prostate, grain lipids, sperm and prostate epithelium.
Elastic fibers found in urine sediment with pus or blood when necrotic processes and small pieces of tissue at neoplasms, and tuberculosis, abscesses and urinary organs, etc..
Elements of tumors They are often found in the urine as a sediment, and in small scraps plotnovata bladder cancer, uterus and cervix or penis, and renal cancer, Wilms tumor and other, sometimes together with elastic fibers and crystals gematoidina.
Giant cells Pirogov-Langhans often found in the urine, along with the collapse of the caseous tuberculosis of the urinary organs. In preparations, made from the urine sediment or fabric scraps, where these elements have been found, often and in large quantities are found Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Uretralʹnye or in the urine usually occur in chronic urethritis Their length ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The easiest way to find them in the first 10-15 ml morning urine. These structures consist of mucus, white blood cells and epithelial cells of the urethra.
Depending on the number of leukocytes urethral mucous threads may be or mucopurulent. The epithelium of the mucous threads dominates the urethra in the form of large clusters or layers of light flattened cells nezernistyh, observed a small amount of white blood cells.

The muco-purulent filaments are many white blood cells, covering all or most of the field of view, and a minor amount of certain epithelial cells and erythrocytes sometimes unmodified.
Elements of unorganized urine sediment
The precipitate urine, consisting mainly of salt, It called unorganized. Some of the salts can be recognized with the naked eye:
- whitish precipitate consists of amorphous phosphate;
- -from pink amorphous urate;
- brick red crystal - uric acid;
- Crystal whitish-of tripelfosfatov etc..
With greater certainty the nature of the precipitate detected by microscopic examination, and in cases of doubt - as a result of chemical reactions.
Chemical examination of urine sediment It should be performed in a centrifuge tube, which after centrifuging and decanting the supernatant urine sample is added to the precipitate or other reagent. Mikrohimičeskie reactions hosts on the subject acquired through the draft mix drops drop of reactives. The preparation is then covered with a cover glass and examined under a microscope. At the same slide is placed next to a drop of the sediment without reagent and the other covered with a cover glass. Both drugs under microscope, observing changes in the preparation, to which the reagent is added.
