Eczema – Atopic dermatitis
Description of eczema
Eczema – chronic inflammation of the outer layers of the skin, which most often occurs in infants and children. Sometimes it can also occur in adults. This disorder is not contagious. Eczema also known as atopic dermatitis.
Causes of eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. Factors, which may cause eczema, include:
- Genetics;
- Environment;
- Allergy – can include allergic reactions to things, which relate to the skin (eg, wool or flavorings in soap), allergies to dust mites (Often), or food allergies;
- Stress, particularly if they lead to scratches;
- Frequent washing of affected areas;
- Use of rubber gloves in persons sensitive to latex;
- Scratching or rubbing of skin.
Risk factors
Factors, which increase the likelihood of eczema:
- Age: five years old or younger;
- Bronchial asthma or hay fever;
- Urban areas or places with low humidity;
- Relatives, which have eczema or allergic diseases;
- Race: negros and Asians.
Symptoms of Eczema
Symptoms may be different in different individuals. Brushing and rubbing can cause or aggravate some of the symptoms. Symptoms include:
- Dry, itching;
- Cracks behind the ears or in other skin folds;
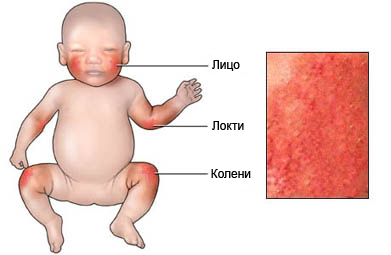
- The rash on the cheeks, hands and feet;
- Red, cheshuychataya skin;
- Heavy Leather;
- Small, raised bumps on the skin;
- Crusted, cracked, or peeling skin;
- Worsening in the winter, dry indoor air.
Diagnosis of eczema
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. The patient may be referred to specialists for further examination. A dermatologist specializes in skin diseases, allergist – of allergiyah.
Treatment of eczema
The main goals of eczema treatment are:
- The treatment of the skin and preserve it healthy;
- Termination scratching or rubbing of the skin;
- Avoid contact with skin infection;
- Preventing flare;
- Avoiding allergens, eczematogenous;
- Avoid scratching.
Treatment options may vary. The doctor may recommend one or more depending on the condition of the patient. Treatment of eczema include:
Skin care
- It is necessary to avoid prolonged use of a hot bath or shower. Reception time necessary to limit the 15-th minute;
- Using a mild soap or detergent without soap can help prevent eczema;
- After bathing or water treatments must be dry and apply moisturizer;
- It is necessary to treat skin infections as soon as they become available.
Medication
- Creams and ointments, containing cortisone, tacrolimus or pimecrolimus;
- Oral formulations (eg, prednisone or cyclosporine) – for severe cases of eczema;
- Antibiotics – applied directly to the skin or taken orally (only for the treatment of infections);
- Antihistamines- to help prevent itching.
Phototherapy
- Treatment with ultraviolet light – performed by a qualified physician;
- Photopheresis – in severe cases of eczema.
Profilatika eczema
Eekzemu difficult to prevent, especially in the case of family histories. Possible to reduce the risk of eczema in a child:
- It is necessary to use breastfeeding;
- For infants, feeding mixtures, you need to use a certain kind of food, comprising 100% serum proteins;
- It is recommended to take probiotics during pregnancy and after childbirth (breast-feeding).
The doctor can provide more information on measures to reduce the risk of eczema.
If the patient already has eczema, you must try to control it:
- It is necessary to take measures to destroy dust mites;
- It is necessary to avoid direct skin contact with wool;
- Some plants can cause deterioration of eczema. It is necessary to avoid them;
- It is necessary to apply a moisturizer, if the skin is too dry;
- It is necessary to avoid scratching or rubbing, where possible;
- The room needed to maintain a constant level of humidity;
- It is necessary to avoid emotional stress.
