Mastopatia – Benign mammary dysplasia
All varieties of breast dysplasia are dishormonal hyperplasia. They are characterized by proliferative, degenerative and metaplastic- of processes and changes in the epithelium d cooler. There are incomplete filling- ferativnuyu and benign proliferative dysplasia (mastopatiю) .
Nonproliferative breast breast
Depending on the nature and localization of the pathological process, the following types of non-proliferative mastopathy:
- lobular;
- ductal;
- cystic;
- fibrous.
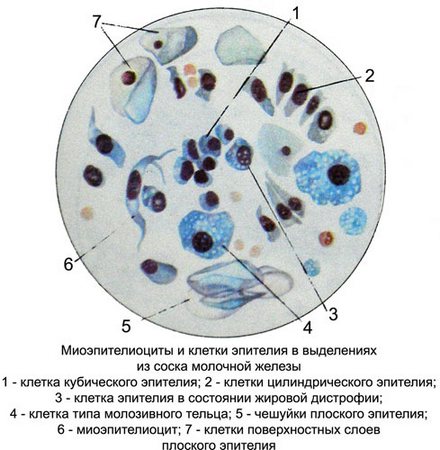
When nonproliferative mastopathy from the nipple of the breast during extrusion stands molozivopodobnaya liquid or creamy thick mass of gray or brown. When fibrous mastitis allocating scarce, serous nature. Macroscopic and microscopic picture punctates scrapings and depends on the place of their receipt (uchastok sclerosis, advanced cystic duct, atrophic lobule and others.).
On microscopic examination, on a background of scant amorphous mass, fine disintegration, drops of fat and cholesterol crystals and cubic cells are found columnar epithelium of the milk moves.
The epithelium of the ducts of the breast unaltered, monomorphic, as well as the phenomena of steatosis, vakuolizaciej, pyknosis of the nucleus. In a small number of cell types identified colostric cells, stellate myoepitheliocytes, tissue basophils, plasma cells, gistiocitы, macrophages, neutrophilic granulocytes, lymphocytes, and fibrocytes, which are located separately and bundles.
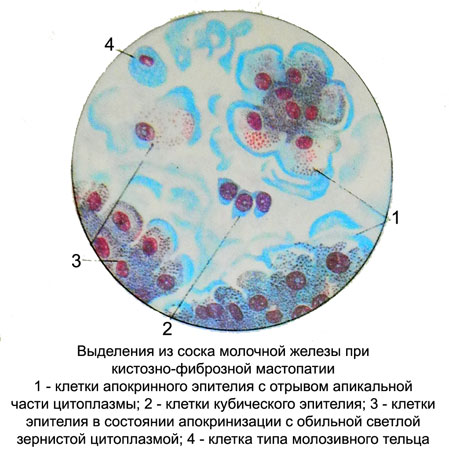
If you get a needle into the cyst cavity receive abundant material with small scraps of fabric. At microscopy besides the usual elements, characteristic of non-proliferative mastopathy, It found often located layers and flattened ferrous (apocrine) epithelium, in which cystic mastopathy differentiate with other types of mastitis.
Epithelial, lining the walls of the cyst, It is in apocrine secretion and morphological characteristics significantly different from proliferating cubic elements and columnar epithelium.
Cells with signs apokrinizatsii bright, big, different shapes (irregular and round, oval, cylindrical), with a predominance of high prismatic epithelial cells.
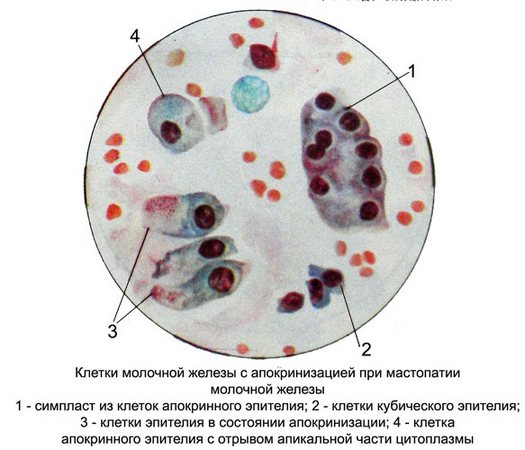
The cell nuclei are small, monomorphic, rounded, less oval, eccentrically located in the cell. There are cells with large nuclei. Chromatin filamentous or melkoglybchaty, evenly distributed, stained with different intensities, often a light purple shades. The contours of the nuclei straight, clear. In many cores there are small isolated nucleoli. The cytoplasm is abundant, painted unevenly. Often it is near the core basophilic, painted in dark colors, and on the periphery oxyphilous, pale or barely visible, in other cells around the nucleus - pale, and on the periphery of the high colored. Thus, The cytoplasm of these cells is often a two-layer, often with a margin of the apical part.
Proliferative breast breast
Proliferative breast disease characterized by epithelial, myoepithelial and fibroepithelial proliferation of the milk ducts and lobules of the breast. Metaplazirovanny epithelium characteristic of cystic cavities.
Mioэpitelialynaya proliferation prevails when sclerosing adenosis (myoepithelial tumor). Outbreaks fibroepithelial proliferation and the formation of small tsistadenopapillom fibroadenomas accompany all types of proliferative mastopathy. However, large fibroadenomas acquire independent significance and are benign tumors.
Cytograms for different types of proliferative mastopathy similar, so the differential diagnosis of difficult. Cytology only allows to determine the degree of proliferation (moderate, pronounced, premalignant) and the nature of metaplasia (flat epithelium and apokrïnnıy). Finding metaplazirovannogo epithelium indicates the presence of a cystic cavity, and the presence of papillary bizarre branching complexes indicates intraductal papilloma. Cytograms when glandular mastitis and fibroadenoma of the breast are not differences.
Discharge from the nipple of the breast during the proliferative mastitis Meager, clear, serous nature, grayish yellow. In the presence of cysts and ductal proliferation allocation sanioserous. Punctate and scraping neobilnye, also sanioserous nature with small scraps of fabric.
Microscopic examination in the case of proliferative mastitis and fibroadenoma revealed various cellular elements.
In moderate proliferation without atypia cells increased the milk ducts, intensely colored, incorrect, cubic, cylindrical or elongated.
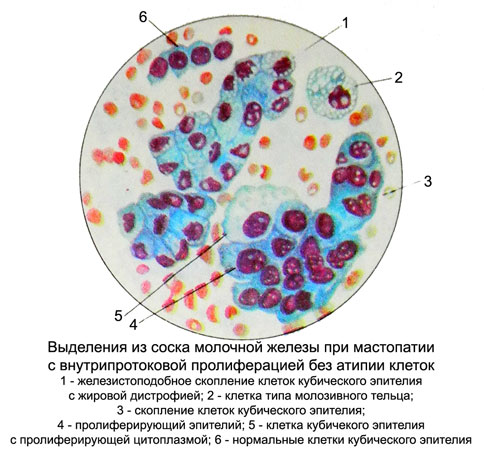
Cores of coarsen, become round, oval and elongated, may become hyperchromic.
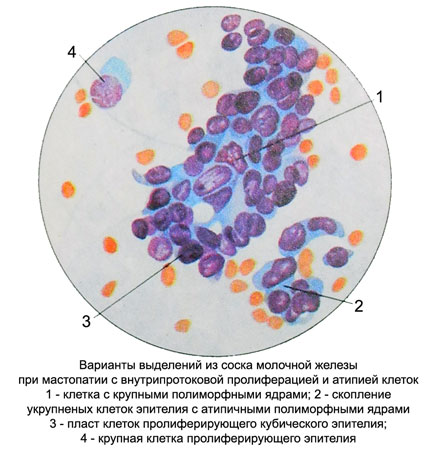
In most of the nuclear hypertrophy nucleoli. Enhanced basophilia of the cytoplasm, it appears fine granularity in a small amount. Sometimes proliferating epithelium stained paler normal. There are some large cells with extensive, sometimes foamy or vacuolated cytoplasm and nuclei slightly enlarged.
Prevailing in moderate proliferation without atypia are the same type cells and nuclei of normal nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio. The contours of the nuclei straight, clear, delicate chromatin network, often normochromic. Arranged in isolation cells, clusters and zhelezistopodobnymi groups in the form of strands, buds with dense arrangement of cells and multi-layers with indistinct borders and in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells randomly arranged.
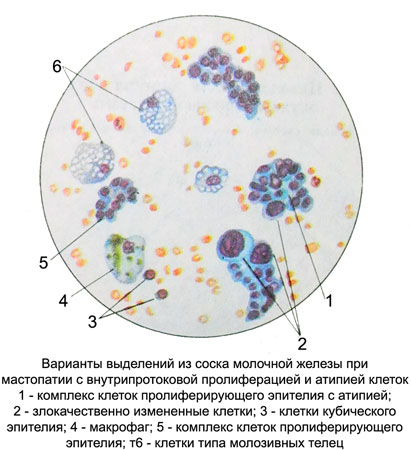
Papillary epithelial proliferation of the milk ducts and lobules of the breast are often subjected to malignancy.
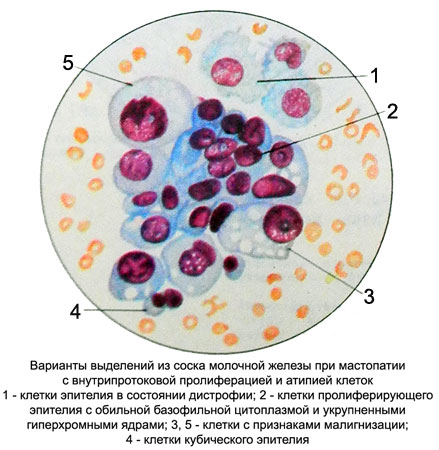
Stellate myoepitheliocytes with proliferating epithelium of the milk sinuses and apocrine epithelium proliferation in the focus of sclerosing adenosis (mnoepitelialnoy tumor). As the transition sclerosing adenosis in fibrotic stage in cytological preparations increases the number of fibroblasts and fibrocytes.
Papillary complexes of apocrine epithelial cells and ducts characteristic of tsistadenopapillom in the centers fibroepithelial proliferation. Lots fibroepithelial proliferation are often subjected to malignancy.
In punctates breast or discharge from the nipple when fibroepithelial proliferation, as in fibroadenoma, They found the same type, preferably the same size and shape of the cubic and prismatic epithelial cells of round shape with the same round or oval nuclei. The cores contain delicate chromatin structure, intensely colored, 1-2 comprise small, the correct form of the nucleolus. The cytoplasm is narrow, Homogeneous, basophilic. Arranged in isolation cells, in the form of clusters, formations, symplast, zhelezistopodobnyh structures, microscopically small fabric scraps. Usually, meet and fibroblasts and cells such as cells colostric. Fibroblasts are placed in isolation, groups and bundles.
For all types of proliferative mastopathy found a significant number of cells such as cells colostric, tissue basophils, macrophages, plasma cells, marked clusters of lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It can detect a different number of red blood cells. When fibroadenoma unlike fibrous mastitis listed cells are absent.
