Bullae or large blisters: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Bubbles
What are bullae?
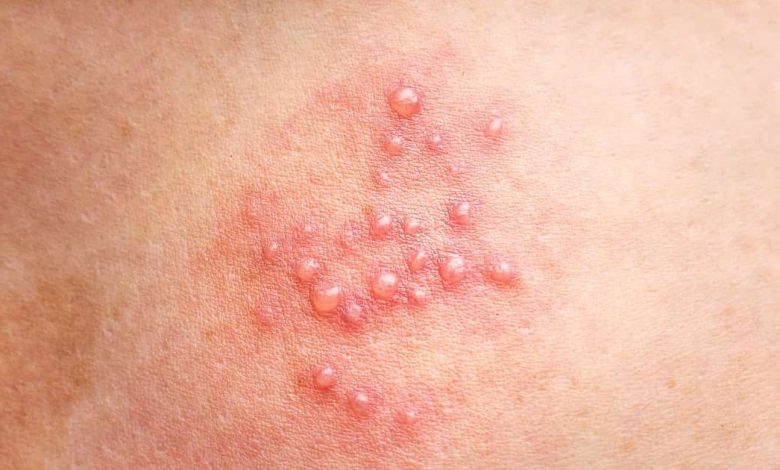
Bullae are large fluid-filled blisters, that form on the skin. They are usually caused by a skin condition., eg, burn, infection or allergic reaction. Bullae can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.. They can be painful and uncomfortable., itching and burning. In some cases, the bullae can become infected and lead to more serious complications..
Causes of bullae
Bullae can be caused by a variety of conditions., including:
- Burns: bullae can form as a result of a burn, eg, sun or chemical burn.
- Infection. Bullae can form as a result of bacterial, viral or fungal infection.
- Allergic reactions: bullae may form as a result of an allergic reaction to a substance, such as medicine or food.
- Autoimmune diseases: bullae may form as a result of an autoimmune disease, such as lupus or pemphigus.
- Skin diseases: bullae can form as a result of skin diseases, such as eczema or psoriasis.
bull symptoms
The most common symptom of bullae is the presence of large blisters on the skin., fluid-filled. These blisters can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.. They can be painful and uncomfortable., itching and burning. In some cases, the bullae can become infected and lead to more serious complications..
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you have bulls, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. It is especially important to contact a healthcare professional, if the bullae are painful, if they are accompanied by other symptoms or if they are infected.
Questions, that your doctor may ask
When you visit your doctor for a bull, he can ask you a lot of questions, including:
- Where are bullae located?
- How long have you had bullae?
- Are bullae painful??
- Bullae itch or burn?
- Have you had any other symptoms, such as fever or chills?
- Have you recently been exposed to a chemical or other irritant?
- Have you recently taken a new medicine or food?
- Do you have other diseases, such as diabetes or an autoimmune disease?
bull diagnostics
To diagnose bullae, your doctor, probably, perform a physical examination and ask you questions about your symptoms. He may also order tests., such as a skin biopsy or blood test, to confirm the diagnosis.
Bull treatment
Treatment for bullae will depend on the underlying cause.. In some cases, bullae may disappear on their own without treatment.. Other cases may require treatment. Treatment options may include:
- Medicines for topical use. Medicines for topical use, such as corticosteroids or antibiotics, can be used to reduce inflammation and treat infections.
- Oral formulations. Oral formulations, such as antihistamines or immunosuppressants, can be used to reduce inflammation and treat infections.
- Surgical intervention: in some cases, surgery may be required to remove the bullae.
bull home treatment
In addition to medical treatment, there are several home treatments, which can help reduce the symptoms of bulla. These include:
- Keeping the affected area clean: it is important to keep the affected area clean, to prevent infection.
- Applying cold compresses: applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Medication, otpuskaemыh without prescription. Medicines, otpuskaemыe without prescription, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Avoid irritants: it is important to avoid any irritants, such as soap, detergents or perfumes, which can worsen symptoms.
Be preventative
In some cases bullae can be prevented. To reduce the risk of developing bullae, important:
- Avoid exposure to irritants: important to avoid exposure to irritants, such as soap, detergents or perfumes, which may cause an allergic reaction or irritation.
- Wear protective clothing: outdoors it is important to wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and trousers, to protect the skin from the sun and other irritants.
- Avoid contact with infected people: it is important to avoid contact with people, who have an infection, such as a cold or flu, to reduce the risk of infection.
- Observe the rules of hygiene. It is important to follow the rules of hygiene, eg, wash your hands frequently, to reduce the risk of infection.
- Seek medical advice: If you are experiencing any symptoms of bull, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Used sources and literature
Dinulos JGH. Principles of diagnosis and anatomy. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif’s Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide in Diagnosis and Therapy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Dinulos JGH. Vesicular and bullous diseases. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif’s Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide in Diagnosis and Therapy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
