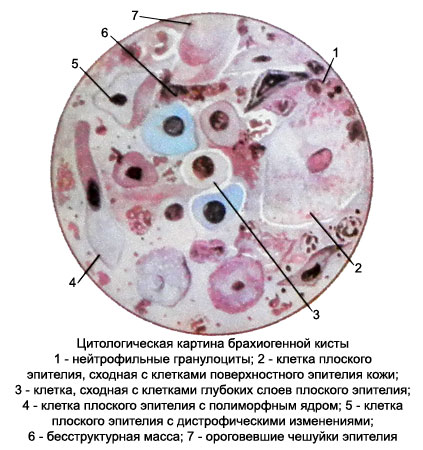
Branchial cyst, branhiogennыy cancer – Cytological diagnosis
Branchial cyst
Branchial cyst there still is not completely obliterated the gill apparatus, or the remnants of the thymus-pharyngeal duct. Located under the skin, deep in the muscles of the middle line or at the front edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The tumor may be up 10 cm diameter. There are ecto- and endodermal cyst.
Ectodermal cyst
Ectodermal dermoid cyst has a structure. It is characterized by the presence of epithelial lining, follows the structure of the skin, with all its appendages. The cyst may contain cellular detritus, horny scales, hair, sebum. The walls of the cysts sometimes there are areas of bone and cartilage. Punctate a cyst looks yellowish-gray or murky liquid dough. On the surface, punctate may be a brilliant film, due to the presence of multiple cholesterol crystals.
Microscopic examination of native drugs on the background of structureless mass revealed a large number of cells flat epithelial stratum and neorogovevayuschy, settling down and chaotic heap of layers, the remains of the destroyed cells, including "naked" nucleus.
There may be cholesterol crystals, in the presence of pearlescent punctate deposits on the surface - in a large amount. In the case of acceding inflammation detected neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages and other typical cellular elements.
In stained preparations flat horny cells, chaotic conglomeration of epithelium slightly perceive color and so poorly reviewed.
Endodermal cyst
Endodermal cyst lined by ciliated columnar epithelium, which are located under the accumulation of lymphoid cells - follicles. The contents of the mucous or serous cysts. Punctate tumor liquid mixed with blood or mucous-bloody. It can detect tiny grayish fabric scraps.
Microscopic examination revealed a high prismatic epithelial cells, and groups which are located separately, and cells of lymphoid tissue, as mature, and their precursors.
Branhiogennыy cancer
Branchial cancer is localized in the sides of the neck. Primary branchiogenous cancer develops from the remnants of the epithelium of gill arches, secondary - is the result of malignant transformation of branchial cysts. Rarely, any age.
Punctate tumor looks friability weight grayish-yellow.
Microscopic examination against the background of structureless mass balances and destroyed cells there is a large number of cells of stratified squamous epithelium, among which are found polymorphic squamous cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei and cytoplasm of various widths and colors, sometimes having at the edges of the glassy nature of.
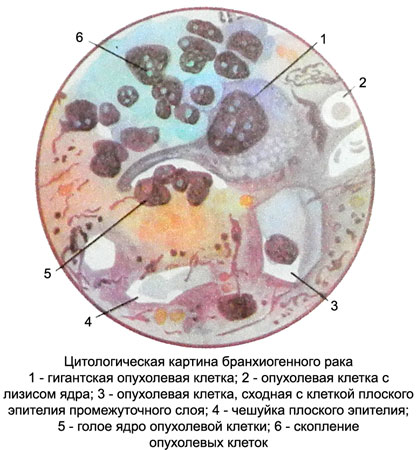
There are also giant, dramatically abnormal cells. Symptoms of fatty degeneration observed in most cells, lymphoid elements are rare.
Branchial cancer diagnosis It is made only in the case, When is a possibility of metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the other body. The presence in a punctate tumor glandular structures along with lymphoid elements can not put cytologic diagnosis branchial cancer.