Shoulder pain: What's it, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Shoulder pain; Pain – shoulder
Shoulder pain: What's it?
Shoulder pain is a common symptom, which can occur due to various medical reasons. This symptom may restrict movement, cause discomfort and reduce the patient's quality of life. It is important to understand, that shoulder pain can be due to a variety of conditions, from injuries and inflammatory diseases to spinal pathologies.
Causes of shoulder pain
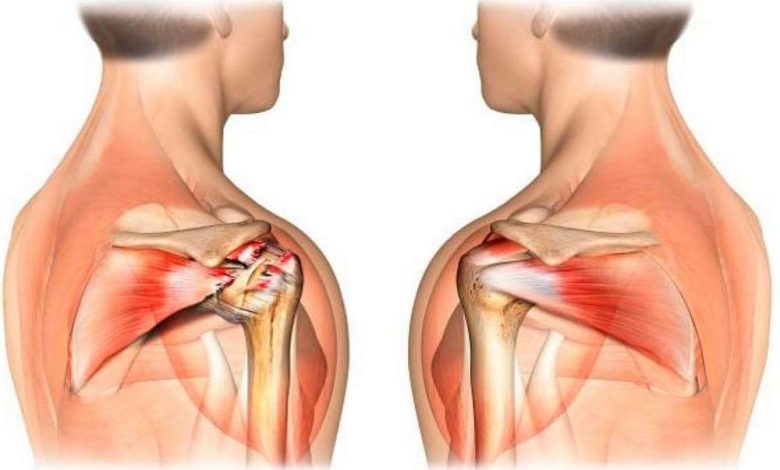
The most common cause of shoulder pain is, when the tendons of the rotator cuff get pinched under the bone in the shoulder. Tendons become inflamed or damaged. This condition is called rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis..
Shoulder pain can also be caused:
- Arthritis in the shoulder joint
- Bone spurs in the shoulder area
- Bursitis - inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa), which normally protects the joint and helps it move smoothly
- Broken humerus
- Dislocated Shoulder
- Shoulder fracture
- frozen shoulder syndrome, which occurs, when the muscles, tendons and ligaments inside the shoulder become stiff, which makes movement difficult and painful
- Overloading or damage to nearby tendons, such as the biceps of the arms
- Nerve damage, which leads to abnormal movement of the shoulder
- Rotator cuff tendon ruptures
- Poor posture and shoulder mechanics
Sometimes shoulder pain can be related to a problem in another area of the body., eg, in the neck or lungs. It's called referred pain. Pain is usually felt at rest and does not worsen with shoulder movement.
Shoulder pain symptoms
Shoulder pain symptoms may include:
- Sharp or dull pain: The pain may be a sharp stabbing sensation or a dull ache, which increases with movement..
- Limited range of motion: Pain may interfere with normal movement of the shoulder and arm.
- Discomfort at night: Pain may get worse at night, especially in certain body positions.
- Numbness or tingling: There may be numbness or tingling in the arm and shoulder.
When to see a doctor
Sudden pain in the left shoulder can sometimes be a sign of a heart attack.. Call the number 911 or local emergency medical number, if you suddenly have pressure or squeezing pain in your shoulder, especially if the pain radiates from the chest to the left jaw, arm or neck or is accompanied by shortness of breath, dizziness or sweating.
Contact the hospital emergency department, if you are seriously injured, We have an accident, and your shoulder is very painful, swollen, bruised or bleeding.
Call your doctor, if you have:
- Shoulder pain with fever , swelling or redness
- Shoulder motion problems
- Shoulder pain does not go away for more than 2-4 weeks, even after treatment
- Shoulder swelling
- Red or blue color of the skin of the shoulder area
Questions, which the doctor may ask
Your doctor may ask you the following questions to better diagnose and determine the cause of your shoulder pain:
- What is the nature of the pain? Describe the pain: sharp, blunt, pricking?
- When the pain started? Whether there was a previous injury or other factors?
- Is there a movement restriction? Can you lift and move your shoulder freely?
- Are there associated symptoms? For Example, numbness, weakness or pain in other parts of the body?
Shoulder Pain Diagnosis
To determine the cause of shoulder pain, your doctor may do the following tests::
- Physical examination: The doctor can evaluate the movement of the shoulder, palpate and check the reaction to painful points.
- Roentgen: Can be prescribed to detect the condition of bones and joints.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) or computed tomography (CT):</ strong> Allows more detailed study of the structures of the shoulder and spine.
- Ultrasound of the joints: The study allows you to assess the condition of the joints and soft tissues.
Shoulder pain treatment
Treatment for shoulder pain depends on the cause of the symptom.:
- Preparations: The doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, pain relievers or muscle relaxers.
- Physiotherapy: Exercises, massage, electrotherapy and other methods can help improve shoulder mobility.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be required, especially with injuries or certain pathologies.
Treating shoulder pain at home
Here are some tips, to help relieve shoulder pain:
- Put ice on the shoulder area 15 minutes, then leave it on 15 minutes. Do this 3-4 twice a day for 2-3 days. Wrap the ice in a cloth. Do not apply ice directly to the skin, because it can lead to frostbite
- Let your shoulder rest for a few days
- Slowly return to your normal activities. A physical therapist can help you do this safely.
- Taking ibuprofen or acetaminophen (eg, tylenol) may help reduce inflammation and pain
Rotator cuff problems can also be treated at home .
- If you have had shoulder pain before, use ice and ibuprofen after exercise
- Learn exercises, to stretch and strengthen the rotator cuff tendons and shoulder muscles. These exercises may be recommended by a doctor or physiotherapist.
- If you are recovering from tendonitis, keep doing range of motion exercises, to avoid frozen shoulder syndrome
- Practice correct posture, so that the muscles and tendons of the shoulders are in the correct position
Prevention
For the prevention of shoulder pain is recommended:
- Maintain proper posture and lifting technique.
- Strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulder girdle through exercises.
- Avoid sudden movements and traumatic situations.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: do sport, eat right and avoid unnecessary stress.
So, shoulder pain can be caused by various factors, and its cause can only be determined by a qualified medical professional. If you have shoulder pain, it is recommended to consult a doctor for diagnosis and prescribing the necessary treatment. Remember, that self-medication may worsen the condition, so it's important to get professional help.
Used sources and literature
Gill TJ. Shoulder diagnosis and decision-making. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, The sink, & Miller’s Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Martin SD, Thornhill TS. Shoulder pain. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell Jr, eds. Firestein & Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 49.
