Atrioventricular septal defect: What's it, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
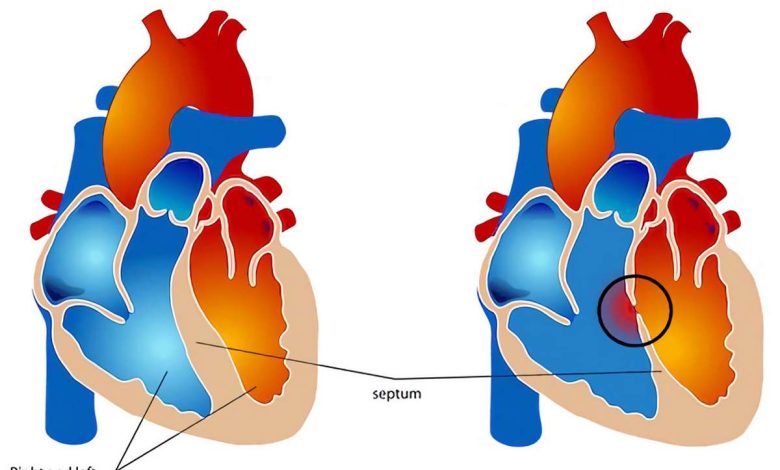
Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
What is an atrioventricular septal defect
Atrioventricular septal defect – heart disease, existing at birth.
The heart has four chambers, that help blood circulate throughout the body. The top two chambers are called atria, and two lower – želudočki. Between the upper and lower chambers are located two valves – tricuspid valve on the right side of the heart and the mitral valve on the left side. Cloth, called partition, divides the chambers and grows, when the fetus develops in the womb.
Atrioventricular septal defect – abnormal growth of tissue, who share a camera. The result is one or more openings, and grows a single valve instead of two separate valves.
Depending on the severity of the defect, the heart is much more difficult to maintain the circulation of blood throughout the body. To correct defects in babies often require open-heart surgery, before damage occurs pulmonary circulation.
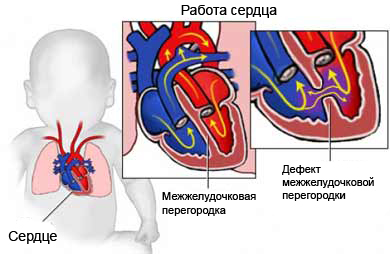
A simple form of atrial septal defect – the hole between the two upper chambers (atria) hearts, which causes the flow of blood directly from left to right, bypassing the ventricles.
Reasons for atrioventricular atrial septal defect
During development in the womb, fabric partitions wrong grows, resulting in an atrioventricular septal defect.
Risk factors
The following factors may increase the likelihood, that the child will be born with atrial septal defect:
- Family history of heart defects;
- Down's syndrome – almost one in five children with Down syndrome have a heart defect is;
- Consumption of alcohol or drug use by the mother during pregnancy;
- Diabetes in the mother;
- Infection with rubella during the first three months of pregnancy;
- Exposure to thalidomide, anticonvulsants, or lithium salts in the development of the fetus in the womb;
- Exposure to certain industrial chemicals during pregnancy.
Symptoms of atrial septal defect atrioventricular
Symptoms include:
- Difficulties with feeding, such as sweating or shortness of breath while eating;
- The difficulty with weight gain;
- High blood pressure in the artery, leading from the heart to the lungs;
- A bluish tint lips and nails, called cyanosis;
- Heart murmur;
- Enlarged heart (seen on chest radiograph).
Diagnosing atrioventricular atrial septal defect
The best way to diagnose atrioventricular septal defect – echocardiography, test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart.
Diagnosis can also be made before the baby is born. The doctor also listens to heart murmurs, Although the noise is not always a symptom. The doctor examines the level of oxygen in the blood, electrocardiogram (test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current through the heart muscle), and performs cardiac echocardiography.
The doctor may use a catheter, to check the blood pressure in the artery, leading from the heart to the lungs. Can be performed a chest x-ray to check for the size of the heart.
Treatment for atrioventricular atrial septal defect
Your doctor may recommend one of the following methods::
- Receiving drugs to strengthen heart, normalize the heartbeat;
- Pacemaker to regulate the heart rhythm;
- Special diet in poor weight gain;
- Current observations of the symptoms and the timely adoption of the necessary measures;
- Depending on the severity of the defect, it may be necessary to limit physical activity;
- Operation in early childhood, to close the opening – recommended, if the defect is severe;
- Diuretics and digoxin to treat heart failure;
- Taking antibiotics before and after surgery, because of the increased risk of bacterial infections.
Prevention of atrial septal defect atrioventricular
Although the disease can not be prevented, because the unknown cause of its occurrence, atrial septal defect can be identified and treated early in pregnancy and childhood. It is recommended to follow these instructions:
- If you have a pregnant or plans to get pregnant, you want to receive prenatal care, eat a well-balanced diet;
- In the presence of diabetes to control blood sugar;
- Avoid drugs, cigarettes and alcohol;
- Prenatal ultrasound, When the fetus 10-14 weeks, It can detect the presence of heart defects;
- If a family has a child with this defect, you need to perform genetic testing, to find out, subject to any future children at risk of the disease.
Used sources
https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/avsd.html
