Arteriovenous malformations
Description arteriovenous malformations
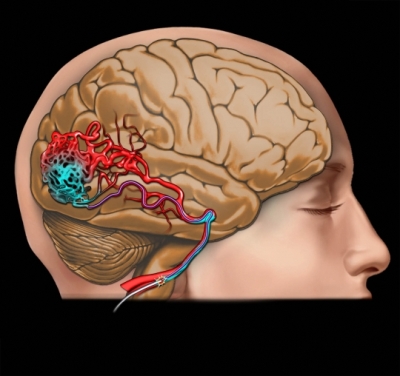
Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) brain and spinal cord arise because of abnormalities of the blood vessels. Arteriovenous malformations can form anywhere, where there are arteries and veins. The most dangerous are those, that form in the brain or spinal cord.
Blood flows through arteries, supplying oxygen from the heart to the brain. Then, the blood enters the smaller blood vessels, which slow down circulation and allow oxygen to get into the surrounding tissue. Finally, veins carry blood, obednennuyu kislorodom, back to the heart and lungs.
Arteries in arteriovenous malformations work otherwise. They feed blood directly into veins through a channel, nazыvaemыy fistula (CVIS), tube-like. Blood, respectively reaches bodies, need oxygen, and high blood pressure in the blood vessels can cause them to rupture.
Two to four percent of all arteriovenous malformations cause hemorrhage or bleeding. Damage, caused by bleeding depends on, where the arteriovenous malformation. If bleeding occurs in the brain, it may be damaged tissue.
Arteriovenous malformations can seriously damage the brain and spinal cord due:
- Reducing the amount of oxygen, reaches the brain;
- The occurrence of bleeding (hemorrhage) tissue, outside the nervous system, including in the brain and spinal cord);
- Squeezing or shift part of the brain or spinal cord.
Complications of arteriovenous malformations include strokes, gidrocefaliû (excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain), spinal cord injury (paralysis), or death.
Causes of arteriovenous malformations
Causes of arteriovenous malformations is unknown. Nonetheless, researchers believe, they arise, when the fetus is developing and the arteriovenous malformations are already present at birth. However, they can also develop and change over time.
Risk factors for arteriovenous malformations
Factors, which increase the risk of arteriovenous malformations:
- Family history – some types of arteriovenous malformations are due to genetic defects, that can be transmitted from one generation to another. People with a family history of arteriovenous malformations are at higher risk of developing;
- Some types of arteriovenous malformations associated with an increased risk of bleeding. People with bleeding occurs for no reason may have a higher risk of having arteriovenous malformations.
Symptoms of arteriovenous malformations
There are a number of symptoms, that may occur in the presence of arteriovenous malformation. Symptoms vary from person to person. They also depend on the location of the arteriovenous malformation in the body.
These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious diseases. If you have any of them to see a doctor.
- Intracranial hemorrhage; It is the most common symptom;
- Convulsions- found in 20% -25% all cases;
- Headache. Headaches are a common symptom, originating in about 15% cases. Sometimes headaches on one side of the head may be a sign of the presence of arteriovenous malformations
- Muscular weakness;
- Paralysis (loss of movement) body parts;
- Dizziness;
- Inability to perform purposeful movements – apraxia;
- Loss of coordination, especially when walking – ataxia;
- Abnormal blood flow sound. This sound, also called noise, can be determined using a stethoscope. It is due to extremely fast flow of blood through arteries and veins at arteriovenous malformation;
- Sudden, severe back pain;
- The difficulties of pronunciation or understanding speech;
- Loss of sensation (hearing, taste, haptics);
- Visual impairment;
- Memory loss;
- Difficulty thinking or mental confusion;
- Hallucinations;
- Imbecility.
Children under the age of two may have different symptoms, including:
- Congestive heart failure (the inability of the heart to pump all the blood, which is returned to him);
- Gidrocefaliя (excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain creates the appearance of a large head);
- Convulsions.
Diagnosis of arteriovenous malformations
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, performs a physical exam. To get a more complete picture of the patient osostoyanii, the doctor may prescribe some tests. Tests may include the following:
- Angiography or arteriography – paint (also called a radiopaque substance) introduced into the artery and performed roentgen, to determine the blood circulation;
- Catheter (very thin, flexible tube) is introduced into the artery until, until it reaches the arteriovenous malformation. The doctor then applies a small amount of radio-opaque dye directly to the place of destruction. Thereafter, the X-rays to study the blood flow in the affected area;
- CT scan (CT) – carried out an X-ray of the head, brain, and / or spinal cord. The procedure is often used for the identification and localization of bleeding. To explore the blood vessels may also be done by CT angiography (CTA);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) – Doctor gets shots brain and spinal cord. MRI is very sensitive and can show the procedure caused bleeding. It can also provide information on the location and physical features of the arteriovenous malformation;
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) – This test involves administering a contrast agent into an artery, and then MRI machine to take pictures.
Doctor, probably, refer to a specialist for further examination and treatment. There are a number of specialists, who specialize in arteriovenous malformations, including neurologist, neurosurgeon.
Treatment of arteriovenous malformations
The goal of treatment is to prevent bleeding, which can lead to strokes. Treatment options include the following:
Medication
Medications may be prescribed to relieve symptoms, such as headache, back pain and cramps. It, However, does not rule out arteriovenous malformation surgery.
Surgery
It is necessary to consult a doctor, to solve, whether the operation is necessary to treat arteriovenous malformation, since its further development can lead to serious complications. Nonetheless, there is always the risk of damage to the nervous system during operation.
There are three different types of operations, each of which will depend on the size and location of the arteriovenous malformation. Types of surgery include:
Normal operation
This type includes performing surgery on that area of the brain or spinal cord, where the arteriovenous malformation is located. This procedure is the most common treatment for arteriovenous malformations.
Endovascular embolization
Endovascular embolization is often used for arteriovenous malformations, which are located deep in the brain. Normal operation can not be performed due to the risk of damage to the surrounding tissue of the brain or spinal cord.
The surgeon holds the catheter through the arteries, until it reaches the arteriovenous malformation. Then, a special substance is introduced into the fistula. This procedure does not destroy the arteriovenous malformation, and reduces the blood flow to her.
Radiohirurgiâ
This procedure uses radiation with a high concentration of radiation, focused directly on the arteriovenous malformation. Radiation destroys blood vessel walls, leading to the arteriovenous malformation. This procedure does not always totally destroy the arteriovenous malformation, especially if it is very large.
Sometimes, arteriovenous malformations better not torogat. It depends on their size and location.
Prevention of arteriovenous malformations
There are no methods, to prevent arteriovenous malformation. But, to reduce the risk of bleeding is necessary to do the following::
- We must avoid actions, increases blood pressure, such as:
- Heavy physical work;
- Smoking;
- It is necessary to maintain a healthy weight;
- It is necessary to drink alcohol in moderation;
- You need to eat healthy foods, contains a lot of sodium;
- It is necessary to avoid blood thinners (eg, warfarin);
- Regular visits to the doctor and a neurologist to check the status arteriovenous malformation.
