Aphasia
Description of aphasia
Aphasia is a communication disorder. It occurs as a result of damage to parts of the brain, who are responsible for language. Aphasia causes impairment in the expression and/or understanding of language, and reading and writing. The earlier aphasia is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment. If you suspect this disease, you should consult a doctor.
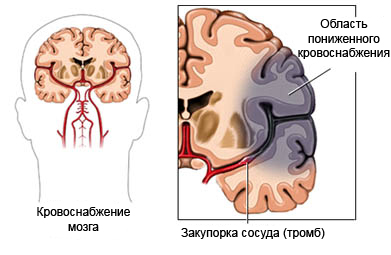
Causes of aphasia
Some causes of aphasia include:
- Stroke (the most common reason);
- Strong blow to the head;
- Gunshot wound;
- Other head injuries;
- Encephaloma;
- Infections of the brain;
- Other diseases of the brain.
Risk factors for aphasia
Factors, which increase the likelihood of developing aphasia:
- Age: closer to the elderly;
- Family history;
- Having last transient ischemic attacks (TIA).
Symptoms of aphasia
Aphasia – a sign of possible brain disease. These symptoms may be caused by other diseases. You must inform your doctor, when did any of them appear.
- Problems in speaking:
- Short, fragmented phrases;
- Putting words in the wrong order;
- Using incorrect grammar;
- Rearranging sounds or words;
- Anomie – problem with word selection (for example, instead of the word “car” it is said “then, what do they drive?”);
- Problems understanding spoken language:
- Need for extra time to understand the language;
- Difficulty understanding quickly spoken phrases;
- Literal understanding of specific figures of speech;
- Reading problems;
- Problems with writing.
Diagnosis of aphasia
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Neurologist, if aphasia is suspected, performs simple tests, which require you to follow commands, answer questions, name objects, and check your spoken language. After this, the patient may be referred to a speech therapist, which will perform further tests, to assess speech and language skills.
Tests may include the following:
- Speech assessment;
- Assessment of the condition of speech muscles;
- Vocabulary and grammar tests;
- Comprehension tests;
- Reading and writing tests;
- Swallowing tests;
- Neuropsychological tests;
- Blood tests;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the head;
- CT scan – X-ray test, which uses a computer to create images of structures inside the head;
- Electroencephalogram – test recording brain activity by measuring electrical current through the brain. This test is performed in some situations;
- Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid – cerebrospinal fluid sample (CSF) taken from the lower back.
Treatment of aphasia
Treatment is aimed at:
- Treating the root cause of aphasia;
- Treating the symptoms of aphasia.
Treatment options for aphasia include:
Speech-Language Therapy
The doctor helps to use the remaining opportunities for communication, to restore lost abilities, learn to compensate for language problems, and learn other ways of communicating. This therapy is carried out individually or in a group.
Family counseling
The doctor recommends to the patient's family, what's the best way to communicate with him?.
Psychological support may also be helpful.
Prevention of aphasia
The most common cause of aphasia is stroke. To reduce its likelihood it is necessary:
- Exercise regularly;
- There are many fruits and vegetables;
- Limit salt and fat intake;
- Give up smoking;
- Moderately consume alcohol;
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Monitor your blood pressure;
- Consider taking low-dose aspirin, if the doctor recommends it;
- Seek medical help immediately if you have stroke symptoms.
