Aortalnыy stenosis in children – Aortic stenosis children
Description of aortic stenosis in children
The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta (the largest artery in the body), that supplies blood throughout the body. Aortalnыy stenosis – narrowing aortic valve, which can block blood flow from the heart and cause an increased pressure in the heart and lungs. Aortic stenosis may vary from mild to severe. In children, it is most often a congenital disorder. It means, that a child is born with this disease. Its origin may be due to genetic problems, the environment, or appear randomly.
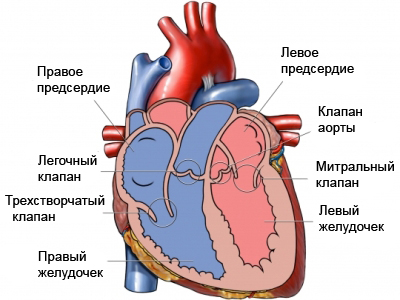
The causes of aortic stenosis in children
The main causes of child aortic stenosis include:
- A birth defect of the aortic valve, which typically consists of three segments;
- aortic valve, which has only one segment or other defects from birth;
- Improper closure of the aortic valve.
Damage to the aortic valve may cause some infections:
- Rheumatic fever (usually, occurred after streptococcal infections);
- Bacterial endocarditis.
Risk factors
Factors, which increases the risk of child aortic stenosis:
- Having a family member with heart valve disease;
- The presence in the past rheumatic fever or bacterial endocarditis.
Symptoms of aortic stenosis children
If a child has aortic stenosis, it may be asymptomatic. With age, the following symptoms may develop:
- Fatigue after exercise or stress;
- Fainting during physical exertion or stress;
- Pain, compression, pressure, or chest tightness, usually, arising from stress;
- The sensation of rapid or irregular heartbeat;
- Breathlessness;
- Dizzy with tension.
In rare cases,, Stenosis can cause:
- Abnormal heart rhythm (aritmiju);
- sudden death, having no symptoms.
Diagnosing children aortic stenosis
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, performs a physical examination. Symptoms of aortic stenosis can be seen by the following reactions:
- Abnormal sounds in the chest, such as a heart murmur;
- Noticeable vertical pitching and vibration chest, when the doctor hand on heart.
To confirm the diagnosis, Tests may include:
- Chest X-ray, to photograph the structures inside the breast;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Stress test – record activity of the heart during physical exercise;
- Heart catheterization (rarely performed) – after the administration of contrast agent is an X-ray of the heart.
Treatment of infantile aortic stenosis
If your child has a mild form of aortic stenosis, his condition will be monitored, and, perhaps, immediate treatment is needed.
Lifestyle changes
If your child has a form of aortic stenosis of moderate to severe, your doctor may advise him to avoid strenuous physical activity. For Example, the child can not participate in sports competitions.
Medications
If necessary,, child medication may be prescribed, to prevent heart failure. In some cases, the child must take antibiotics before a visit to the dentist or the performance of surgical procedures. This is to prevent infection, that can affect the heart.
surgery
Operation
Severe form of aortic stenosis may require surgery. The operation includes the following options:
- Bologna alvuloplastika – device in the form of the ball passes through the artery, to open or enlarge the aortic valve. It can provide relief of symptoms. Since the valve can be blocked again, this operation, perhaps, I have to repeat;
- Replacement of the aortic valve – surgical replacement of a defective heart valve.
Prevention of child aortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis is a congenital disease, therefore, its appearance can not be prevented.
