Aortic regurgitation
Description aortalьnoй regurgitation
Aortalьnaя regurgitation Heart – disease, at which the valve between the left ventricle (lower left chamber of the heart) and the aorta (the main blood vessel) damaged. Defect valve causes blood to flow back pumpable heart. As a result,, the left ventricle must work harder, to pump more blood, than usual. This gradual increase in load leads to, that the left ventricle can increase in size. There are two main types of aortic regurgitation:
- Acute aortic regurgitation – Symptoms develop rapidly, have severe consequences, prompt surgical intervention can save lives;
- Chronic aortic valve – Symptoms develop over months or years.
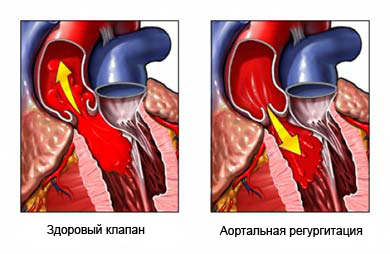
Prichinы aortalьnoй regurgitation
Possible structural causes of aortic regurgitation:
- The aortic valve itself is deformed;
- Deformation of the heart near valve or disorder affects its operation.
Risk factors
A risk factor is something, which increases the likelihood of disease.
Acute aortic regurgitation
Risk factors for developing acute aortic regurgitation include:
- Infections of the heart, such as:
- Rheumatic fever;
- Infective endocarditis;
- Aortic dissection – separation of the inner layer of the aorta from the middle layer;
- Trauma, eg accident.
Chronic aortic valve
Risk factors for developing chronic aortic valve regurgitation include:
- Bicuspid aortic valve – Congenital (suschestvuyuschae birth) strain, at which the aortic valve has two segments, instead of three;
- Other types of congenital heart defects;
- Infections of the heart, such as:
- Rheumatic fever;
- Infective endocarditis;
- Disease, which cause expansion of the base of the aorta, such as:
- Marfan syndrome;
- High blood pressure;
- Collagen vascular disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Aneurysm aortы;
- Paul: male;
- Age: senior 50 years.
Simptomы aortalьnoй regurgitation
In acute aortic valve regurgitation symptoms occur rapidly, because the heart is no time, or to compensate to increase blood flow. In chronic aortic valve regurgitation symptoms develop gradually and may not be visible for many years.
In both cases, the symptoms may include:
- Breathlessness;
- Fatigue, especially after physical activity;
- Fluid retention in certain parts of the body, eg, ankles;
- Cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat);
- Angina (chest pain from insufficient blood supply);
- Hypotension (low blood pressure).
Diagnosis aortalьnoй regurgitation
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, performs a physical examination. In particular, the doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to heart murmurs. If there is a certain type of heart murmur, a doctor may suspect, the presence of aortic regurgitation and may recommend further tests, such as:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Chest X-ray, to determine the approximate size and shape of the heart. When aortic regurgitation chest x-ray may show enlargement of the lower left ventricle, and in some cases, and expansion of the aorta;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart. It can detect leaking valves and abnormal thickening of the heart muscle. This test can also examine the functioning of the left ventricle;
- Heart catheterization – special tube inserted into the heart through an artery (usually in the groin), to detect a problem with the structure of the heart, its function, and blood supply;
- Radionuklidnaâ ventrikulogramma (a nuclear scan) – measures, how well the left ventricle pumps the blood, and the amount of blood, is pumped from the ventricle with each heartbeat.
Treatment aortalьnoй regurgitation
In the case of severe acute regurgitation of blood in the aortic valve, especially due to injury, It may be required emergency surgery.
In chronic regurgitation of blood during aortic valve choice of treatment depends on several factors. They include:
- How to develop symptoms and how severe they are;
- The degree of heart disease and the level of heart function;
- Age;
- Risks, associated with treatment;
Treatment for aortic regurgitation may include:
Medication
If aortic regurgitation is not causing symptoms and heart function remains normal, can be used drugs, lowers blood pressure. Medication may also be administered to treat pain in chest, for the treatment of irregular heartbeat, to prevent infection of damaged or artificial valves, as well as to prevent blood clots.
Operation
The operation is usually performed for severe acute aortic regurgitation cases or for some cases of chronic aortic regurgitation. If you have chronic aortic regurgitation, the physician monitors the symptoms and heart function in order to determine the best time for surgery. The operation includes replacement of the aortic valve.
Prevention aortalьnoй regurgitation
Prompt treatment of streptococcal infections can prevent rheumatic fever, which is a risk factor for problems with heart valves, Takima how aortalьnaя regurgitation. Patients should talk to your doctor, to understand, In some cases, you may need to take antibiotics, to reduce the risk of infection of the valve. For Example, It may need to take antibiotics prior to certain dental procedures or operations.
