Abnormalities, irregularly shaped teeth: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Tooth – abnormal shape; Hutchinson incisors; Abnormal tooth shape; Peg teeth; Mulberry teeth; Conical teeth; Connate teeth; Conjoined teeth; Microdontia; Macrodontia; Mulberry molars
Tooth anomaly refers to any condition, which leads to a deviation from the normal size, the shape or position of the tooth. This may include crooked or misaligned teeth, teeth, that are too big or too small, as well as teeth, who are deformed or have abnormal growth patterns. Dental anomalies can cause discomfort and embarrassment, and may also increase the risk of dental problems, such as cavities and gum disease.
Causes of dental anomalies
Dental anomalies can be caused by a variety of factors., including genetics, trauma and poor oral hygiene. Some people are born with dental abnormalities, while others develop over time.. Some common causes of dental abnormalities include:
- Genetic factors. Dental anomalies can be inherited and can be caused by genetic mutations, affecting tooth development.
- Trauma. Trauma to the teeth or jaw can damage, which results in abnormal growth or position of the teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene. Neglecting to brush and floss regularly can increase your risk of cavities and gum disease, which can lead to dental abnormalities.
- Nutritional deficiencies. Lack of certain vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, may affect tooth development and increase the risk of dental abnormalities.
- Environmental Factors. Exposure to toxins and certain drugs during tooth development can lead to abnormalities.
Symptoms of dental anomalies
Symptoms of dental anomalies may vary depending on the specific condition.. Some common signs of dental abnormalities include:
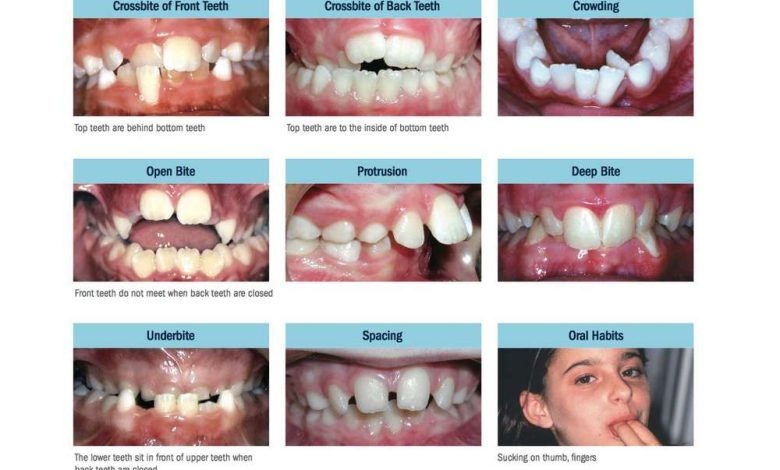
- Crooked or uneven teeth
- Teeth too big or too small
- Deformed or misshapen teeth
- Gaps between teeth
- Crowding of teeth
- Abnormal forms of bite
- discoloration of teeth
- tooth sensitivity
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you have any symptoms of dental abnormalities, it is important to seek medical attention. A dentist or specialist can examine your teeth and diagnose any problems, which may be present. Besides, you should see a doctor, if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe pain or discomfort in the teeth or jaw
- Bleeding or swelling of the gums
- Difficulty eating or talking
- Change in the appearance of your teeth or gums
Questions, that your doctor may ask
During your consultation with your dentist or dental specialist, you may be asked a number of questions, which will help diagnose the cause of your tooth anomaly. Some general questions, that your doctor may ask, include:
- When did you first notice a problem with your teeth?
- Have you experienced pain or discomfort in your teeth or jaw?
- You have a family history of dental problems?
- Have you had any recent trauma to your teeth or jaw?
- Do you have any medical conditions, which may contribute to the problem?
Diagnosis of anomalies of teeth
To diagnose dental anomalies, dentist or dental specialist, usually, performs a physical examination of the teeth and jaws, as well as x-rays or other imaging tests, to get a closer look at the structure of the teeth. In some cases, an impression of the teeth may also be taken., to create a model of teeth for further study.
Treatment of dental anomalies
Treatment options for dental anomalies may vary depending on the specific condition and severity of the problem.. Some common treatment options include:
- Braces or aligners. These devices can be used to straighten crooked or misaligned teeth and improve the overall look of your smile..
- Veneers. Veneers are a thin layer of porcelain, which is applied to the front of the tooth to improve its appearance.
- Crowns. A dental crown is a cap, which is worn over a damaged or deformed tooth, to regain its form and function.
- Orthodontic surgery. In some cases, surgery may be required to correct more severe cases of dental anomalies..
- Removal. In rare cases, tooth extraction may be required., if it causes significant discomfort or cannot be corrected in other ways.
Home treatment of dental anomalies
In addition to professional treatment, there are also some home remedies., which can help manage dental anomalies and prevent further damage. These may include:
- Regular brushing and flossing. Maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent cavities and gum disease., which may contribute to dental abnormalities.
- Avoid hard or chewy foods. Some foods may be harder on teeth and increase the risk of damage or deformity..
- Wearing a mouthguard. If you play contact sports or grind your teeth at night, wearing a mouthguard can help protect your teeth from damage.
- Using fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride helps strengthen teeth and reduce the risk of decay.
Prevention of dental anomalies
Although some dental anomalies are genetic or cannot be prevented, there are steps, you can take, to reduce the risk of developing dental problems. Some tips for preventing dental anomalies include:
- Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, including regular brushing and flossing.
- Eating a Healthy Diet, rich in calcium and other essential nutrients.
- Avoid harmful substances, such as tobacco and excessive alcohol.
- Visit your dentist or dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
Conclusion
Dental anomalies can be a source of discomfort and anxiety, but they can be managed with proper diagnosis and treatment. If you experience any symptoms of dental abnormalities, it is important to see a doctor for evaluation. With proper care and attention, most people can successfully treat dental anomalies and enjoy a healthy, beautiful smile..
Used sources and literature
Dhar V. Development and developmental anomalies of the teeth. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 333.
Moore KL, Persuad TVN, MG press. Integumentary system. In: Moore KL, Persuad TVN, MG press, eds. The Developing Human. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.2020:chap 19.
Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, You AND. Abnormalities of teeth. In: Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, You AND, eds. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2016:chap 2
