Angioedema – Angioedema – Hereditary angioedema
Description of angioedema
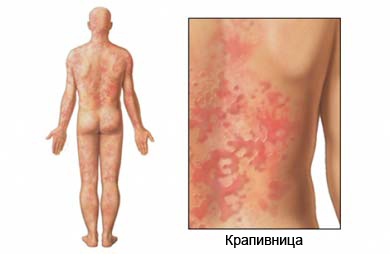
Angioedema – disease, causing swelling under the skin's surface with or without redness. Angioedema can occur around the eyelids and lips, or on the face, hands, legs, genitals. Because this disease can cause swelling of the airway, It is important to promptly seek medical attention.
Causes of angioedema
Angioedema is often associated with urticaria. Her appearance may cause:
- Food (eg, fruit, seafood, nuts);
- Medications (eg, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), ACE inhibitors, BRA inhibitors, penicillin, aspirin, morphine);
- Infection;
- Inhaled substances – pollen, mold spores, animal dander;
- Some diseases – hyperthyroidism, cancer, rheumatism;
- Environmental Factors (eg, cold, heat, water);
- Contact with the skin of plants, animals, or drugs;
- Skin diseases;
- Genetic predisposition.
Risk factors
Factors, that increase the risk of developing angioedema:
- Age: 30-60 years;
- Other conditions:
- Asthma;
- Eczema;
- Hives;
- Paul: female;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Oral NSAIDS;
- Emotional stress;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Menstruation.
Symptoms of angioedema
These symptoms can also be caused by other diseases. You must inform your doctor, if they came any.
- Larger tumors with indistinct borders around the eyelids and lips;
- Lesions on the face, trunk, genitals and limbs;
- Swelling of the hands and feet;
- Swollen throat;
- Abdominal pain;
- Rash, that is not češet′sâ.
Diagnosis of angioedema
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Tests may include:
- Blood tests;
- Urine;
- Skin tests;
- Study of throat infection;
- Fecal;
- Abdominal ultrasound – test, which uses sound waves to study the stomach.
Angioedema treatment
To select the treatment of angioedema should consult with a physician. Small swellings, may not require treatment and disappear, but it is important to make sure, the tumor does not spread to the respiratory tract, swelling which can be life-threatening. Treatment options include the following:
- Medicines – some medications (eg, antihistamines, adrenaline, corticosteroids and painkillers) can help relieve the symptoms of angioedema;
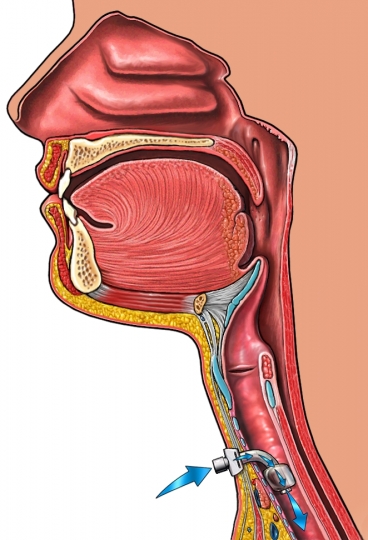
- Tracheostomy – If airway edema arose, dangerous for life, the doctor may place a tube in your throat, to keep the airway open and oxygen was able to get into the lungs.
Prevention of angioedema
To reduce the risk of this disease, There is a need to avoid substances or triggers, which caused hives or angioedema in the past.
