Angina
Description of angina
Angina – pain or discomfort in the chest. Usually its main trait – feeling of pressure in your chest. This condition may be felt in the shoulders, hands, neck, jaw or back. Pain in angina pectoris usually lasts no more than 2-10 minutes. She goes after resting or taking nitroglycerin.
Types of angina include:
- Stable angina is predictable development option. Usually, its intensity and signs of approaching known, and there is time to reduce the negative impact;
- Unstable angina more unpredictable and hard. Chest pain may occur during rest or even sleep (nocturnal angina). Discomfort may last longer and be more intense, than stable angina. Unstable angina may be a sign of a heart attack;
- Variantnaya stenocardia or stenocardia Prinzmetala, It is, When the patient is at rest. This most often occurs in the middle of the night. Its effects can be very serious.
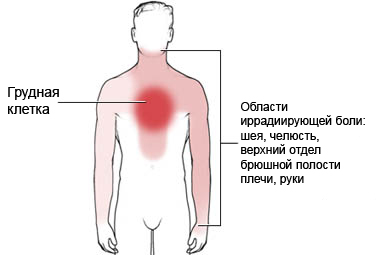
Causes of angina
Angina, usually, is a sign of coronary heart disease (CHD). It arises, When blood vessels, leading to the heart, blocked. Lock reduces the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle. When the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, felt chest pain and other symptoms.
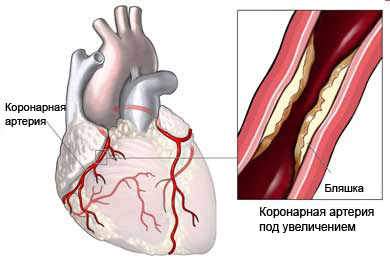
Stable and unstable angina
Angina occurs, When the need heart of oxygen and blood, during:
- Physical exercises, voltage;
- In cold weather;
- After the meal;
- During emotional stress.
Stable angina becomes unstable, when symptoms:
- Meet more often;
- Continue longer;
- Occur faster.
Variantnaya stenocardia and Prinzmetal
These types of strokes are usually caused by cardiac spasm of blood vessels. This may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- Coronary heart disease (CHD);
- High blood pressure;
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- Heart valve disease.
Risk factors
The main risk factors for coronary heart disease include::
- Paul: male;
- Advanced age;
- The presence of family members and relatives with heart disease;
- Obesity and overweight;
- Smoking;
- High blood pressure;
- Passive lifestyle;
- High blood cholesterol (in particular, high LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol);
- Diabetes.
Other risk factors for CORONARY HEART DISEASE:
- Stress;
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
Symptoms of angina
- Pressure or compressive breast pain;
- Some people do not experience severe pain;
- Elderly people, women and people with diabetes are more likely to have atypical symptoms;
- Some patients have vâlotekuŝuû ischemia and do not experience any symptoms and chest pain;
- When any chest pain, you must undergo a medical examination to determine its causes;
- Pain or discomfort in the chest is a distinctive symptom of angina.
The likelihood of heart attack increases, When breast discomfort continues more 15 minutes, and are accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Shoulder pain (shoulders), hand (hands), or in the jaw;
- Weakness;
- Sweating;
- Nausea;
- Breathlessness.
Diagnosis of angina
Tests need to be done immediately, to see, What is the cause of pain – angina or heart attack. If we have a stable pattern of angina, other tests can be made, to determine the extent of the disease. The test results will help you to choose the method of treatment.
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Tests may include the following:
- Blood tests, to look for certain blood markers, to determine heart attack;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – recording of the electrical activity of the heart, to find the signs of heart attack, acute myocardial, or problems with the rhythm of the heart;
- Echocardiogram – high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), used to study the structure and function of the heart;
- Stress test – record electrical activity of the heart during elevated exertion. Sometimes to simulate physical exertion uses special drugs;
- Radiation (nuclear) scanning – radioactive material is injected into a vein, to identify areas with low blood flow;
- Electron-beam (computer) tomography (screening coronary calcium, heart scan, angiography) – types of x-ray examinations, who use computer to create detailed images of the heart, coronary artery and the surrounding structures;
- Computed tomography (CT) measures the amount of calcium deposits in the coronary arteries to determine the risk of cardiovascular disease or heart attacks;
- Some studies claim, that heart scans is most effective in patients with an intermediate risk of coronary heart disease;
- Coronary angiography – x-ray dye is injected into the arteries, you see anomalies (narrowing or blood clots) in the arteries.
Treatment of angina pectoris
Treatment options include:
Medication
- Nitroglycerin – usually taken during the attack of angina pectoris, in the form of capsules under the tongue, or in the form of a spray;
- To prevent strokes can be used long-acting medications, in pill form or in the form of patches (patches) or ointments;
- Blood thinners – slight, daily dose of aspirin reduces heart attack risk;
- For help with angina can also apply warfarin, However, there is an increased risk of bleeding when taking this medication;
- Before daily taking aspirin or warfarin should consult with a physician;
- Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers may reduce the likelihood of strokes;
- Cholesterol-lowering medications can prevent or stop the progression of CORONARY HEART DISEASE;
- Reception of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and blockers receptors angiotenzina (ARB) – reducing blood pressure and decrease the burden on the heart.
Surgery
Patients with severe, unstable, or progressing angina can help the following operations:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting – as a graft artery are used from other areas of the body, to bypass blocked arteries of the heart;
- Koronarnaя angioplasty – used balloon, to open blocked arteries.
Prevention of angina pectoris
If you have angina, you can prevent attack, knowing the symptoms before you.
If no stroke, Prevention of coronary heart disease will help prevent its onset.
Measures for the prevention of coronary heart disease include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight;
- Implementation of safe exercise taking into account the recommendations of the doctor;
- You must quit smoking;
- A healthy diet. It should be low in saturated fat. It should also include whole grains, fruit, and vegetables;
- Timely treat high blood pressure and/or diabetes;
- In time to treat abnormal levels of cholesterol and high triglycerides.
