Anal cancer – Anal cancer
Description of cancer of the anus
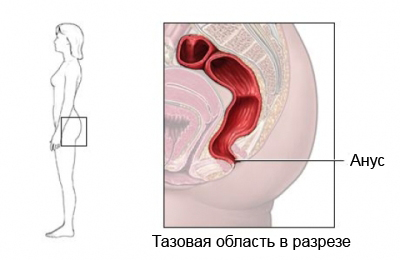
Anal cancer – Cancer of the anus, channel at the end of the colon below the rectum.
Cancer occurs, when the cells of the organism (in this case the cells, that cover the lumen of the anus) divide uncontrollably. Usually, cells divide in an uncontrolled manner. If cells keep dividing uncontrollably, when new cells are not needed, Education appears, called tumor. The term cancer refers to malignant tumors, that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor does not invade or spread to other organs.
Causes of cancer of the anus
The exact cause of anal cancer is not yet clear. But, there is evidence, that the human papilloma virus (HPV) cause of anal cancer cases.
Risk factors
Risk factors include:
- Anal;
- Having multiple sexual partners;
- The presence of HPV infection;
- HIV infection;
- Receiving immunosuppressant;
- Age: senior 50 years;
- Smoking;
- The presence of cervical dysplasia or cervical cancer;
- Low CD4 count (cell, which are part of the immune system).
Symptoms of cancer of the anus
These symptoms may be caused by other diseases. You must inform your doctor, if they came any:
- Anal bleeding;
- Pain or pressure around the anus;
- Itching or discharge from the anus;
- The feeling of firmness around the anus;
- Changes in bowel function;
- Bleeding with bowel movements and without.
Some cases of anal cancer have no symptoms.
Diagnosis of cancer of the anus
The doctor conducts a physical inspection, He asks about the symptoms. Conduct tests, which may include the following:
- Digital rectal examination;
- Anoscopy – examination of the anus and lower rectum
- Proctoscopy – examination of the rectum;
- Transrectal ultrasonography – probe is inserted into the anus and / or rectum, and the doctor can inspect the internal tissues;
- Biopsy – selection of cells to test for cancer in laboratory;
- Roentgen – to take a picture of structures inside the body;
- CT scan – to make pictures of structures inside the abdomen and pelvis;
- PET-тест – vыpolnyayutsya photos, to view the activity of body tissues;
- Combination of CT and PET-test;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- Laboratory tests for the study of bone marrow function, kidney and liver.
Treatment of cancer of the anus
Treatment involves the following procedures:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses special drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs pass through the blood throughout the body, killing cancer cells mostly, but can affect some healthy cells. In the treatment of anal cancer, Chemotherapy is administered, usually, intravenously, once every three weeks during the daily radiation treatment.
Radiation (Radiation) therapy
Radiation therapy is often used in conjunction with chemotherapy. Compared with hirurgiiey, combination chemotherapy and radiation therapy may increase survival.
In some cases, the radiation therapy may be used, If chemotherapy leads to too much side effects (eg, patients with HIV). In the treatment of cancer of the anus is offered daily exposure, during 5-6 weeks.
Since radiation therapy damages healthy tissue, as well as cancer cells, there are certain side effects, associated with the use of radiation therapy for the treatment of anal cancer. In the area of the anus can form scar tissue, preventing anal sphincter function properly. Besides, this type of treatment can lead to chronic bleeding from the rectum.
Operation
Due to the location of the anus, surgery to remove the cancer requires an abdominal resection. This operation leads to a permanent colostomy. Running, if after chemotherapy and radiation again relapse of cancer, or when radiation and chemotherapy, for some reason contraindicated.
Prevention of cancer of the anus
Methods of preventing this disease does not exist. You can reduce the risk of anal cancer, reducing susceptibility to HIV and HPV. There is a vaccine Gardasil, that protects the body from the four types of human papillomavirus.
