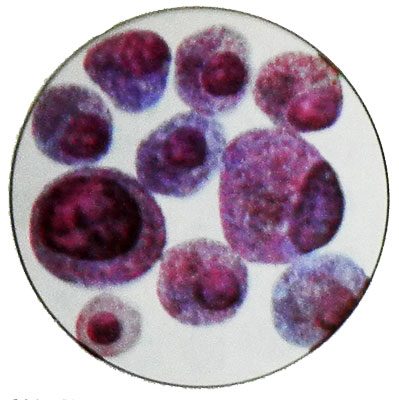
Thyroid adenoma: characteristic punctate thyroid
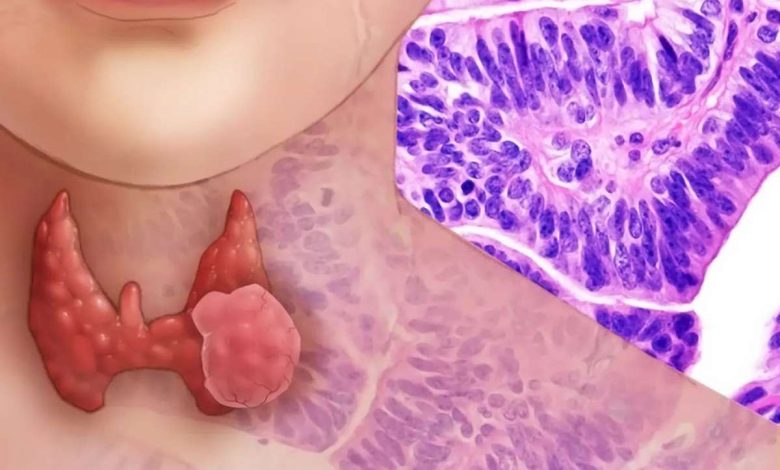
Thyroid adenoma refers to benign tumors. This single, clearly delimited unit (less multiple nodes), capsuliferous.
The cytological picture of thyroid adenoma is characterized by a wide variety of morphological variants., what, apparently, It determined not only by the histological structure, but also the functional state of the thyroid gland and its epithelium. There is a significant similarity cytologic picture in adenoma and goiter, therefore morphologically differentiate these diseases is difficult.
According to the WHO International Classification, Histological structure distinguish trabecular (embryonic), microfollicular (Fetal), makrofollikulyarnuyu (colloidal), papillary, simple and atypical adenoma, and adenoma of B-cells (cell Askanaz).
Trabecular adenoma and microfollicular
Trabecular and microfollicular adenomas develop from thyroid parenchyma and have similar morphological picture. Microscopic examination of the thyroid gland punctate epithelial cells of the same type found small quantities, round and oval, with hyperchromatic, eccentrically located nucleus. The nucleoli are not visible. The cytoplasm of moderate size, Homogeneous, basophilic. The cells are in close contact with each other, forming structures, similar in cytological preparations with tubular formations, turning into a solid field.
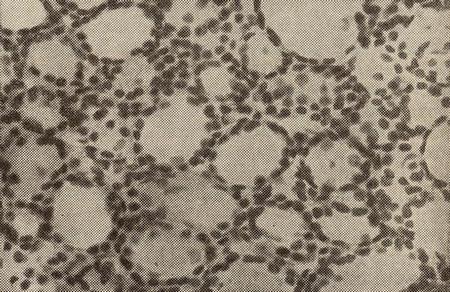
Trabecular, or fetal adenoma less differentiated, Therefore, the inclusion of a colloid in its cells no. When microfollicular, or fetal, adenoma in stained isolated follicles are small size, consisting of monomorphic cylindrical cells, some of whom are dual-core; in some cells detected inclusions - colloid.
Makrofollikulyarnaya adenoma
Makrofollikulyarnaya adenoma characterized by large (to 39 m) flattened, polygonal cells with centrally or eccentrically located nucleus. Chromatin cores melkoglybchaty, with portions of annular structures. Cytoplasm abundant, filled with secretory vacuoles of various sizes and shapes. In some cells marked protrusion portions cytoplasm colloid (apocrine type of secretion). Cells are arranged separately and in the structure of the follicles, sodyerjashikh colloidal.
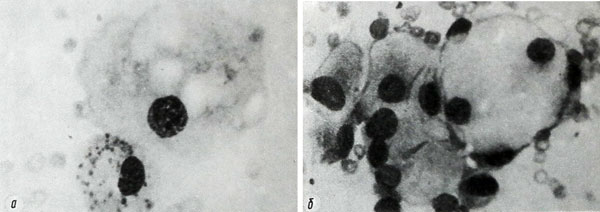
Adenoma of B cells – Adenoma of cells Askanaz – Oxyphilic adenoma
Adenoma of B cells (adenoma cells from Askanaz, oxyphilic adenoma) is dominated by large (to 38 m) эpiteliotsitov. Kernels their round shape, different sizes, located in the center or eccentrically depending on the degree of filling cells secret. The cells, crowded secret, kernel may have meniskoobraznuyu form. There are also dual-core cells.
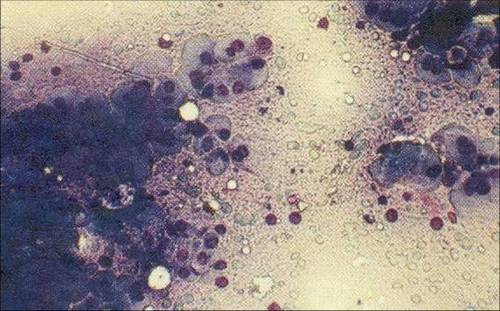
The cytoplasm is abundant, painted in pink, bluish-pink, gray-blue tones and includes a large oxyphilic grainy red or dark purple color, the amount of which varies considerably. Arranged in isolation cells, clusters and groups of zhelezistopodobnyh, palisadopodobnyh and papillary structures.
Simple adenoma
Simple structure and adenoma cell composition close to the structure of the normal thyroid.
Papillary adenoma
Cytology detected a large number of similar follicular cells cubical, located mainly in the form of papillary structures.
Atypical thyroid adenoma
Atypical adenoma is characterized by the presence of follicles of different size and proliferating cells round, oval, elongated and fusiform. Hyperchromatic cell nuclei, and their size often take precedence over the size of the cytoplasm.
When malignancy thyroid adenoma cells in preparations appear with signs of malignancy.