Akromegalija
Description acromegaly
Growth hormone (TOWN) controls the growth of soft tissues and bones of the body. Elevated GH causes an abnormally rapid growth of the organism. In adults, it can result in rare disease – akromegalii. If left untreated it can lead to serious complications and early death.
In children, excess growth hormone causes a deviation, called gigantism.
Reasons for acromegaly
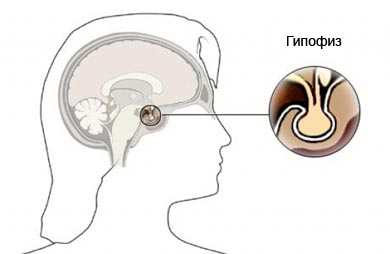
Gipofiz – small iron, located at the base of the brain. It produces many hormones, including growth hormone.
In most cases the increase of GH is caused by a benign tumor of the prostate. Very rarely an excess of growth hormone associated with malignant tumors of other organs (pancreas, adrenal, lungs).
Risk factors for acromegaly
Factors, that increase the likelihood of excess growth hormone:
- Mutations in the genes;
- Average age – 40-45 years.
In some cases, the disease is hereditary and appears in 40-45 years.
Symptoms of acromegaly
Symptoms usually develop very slowly.
In children, the bones grow and appear elongated soft tissue swelling. If untreated, the child can grow up to a height 2 – 2.3 m.
Symptoms and complications in adults may include the following:
Abnormally high growth and deformation:
- Hands;
- Leg (there is a need bigger shoes);
- Person (protrudes the lower jaw and eyebrows);
- Jaws (teeth do not line up in an even number, when the mouth is closed);
- Lips;
- Language;
The emergence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Skin changes, such as:
- Large pimples;
- Excessive sweating body due to the expansion of the sweat glands;
The voice becomes low due to the increase of the vocal cords, and soft tissues of the throat.
- Fatigue, weakness in legs and arms;
- Apnea;
- Arthritis and other joint problems;
- Gipotireoz.
Increase in liver, kidney, spleen, hearts, and / or other internal organs, which may lead to:
- Dïabetw;
- High blood pressure;
- Cardiovascular disease.
Symptoms in women:
- Irregular menstrual cycles;
- Galactorrhea (abnormal production of milk) – about 50% cases.
Symptoms in Men:
- Impotence about 50% cases.
Diagnosis of acromegaly
For the diagnosis, you must first do a physical exam. Often, acromegaly can safely be installed only after a year of onset.
It is necessary to do a blood test to determine the level of these substances:
- Insulin-like growth factor (IAP-R);
Increased production of growth hormone (UVHR) and other pituitary hormones.
The test can be conducted on glucose tolerance, to see, decreases if the level of growth hormone. In the case of acromegaly level will not drop.
If these tests confirm acromegaly, you need to locate the tumor, which causes a disturbance. The wire:
- Computer tomography – X-ray examination using the computer, to take photos of the inside of the brain and surrounding structures;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic radiation, to take pictures of internal body parts, in this case the head.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are as follows:
- Decreased production of growth hormone to normal levels;
- Treating the symptoms, caused by excess growth hormone;
- Treatment of other disorders (Thyroid, adrenal, genital);
- Reducing the size of the tumor.
Treatment may include:
Khirurgiyu
The tumor is removed, that, considered, cause acromegaly. In most cases, the best solution for healing.
Radiotherapy
Radiation exposure is used to reduce swelling. This method is often used, when the operation can not be performed, or medical treatment were unsuccessful.
Medication
Taking certain drugs may decrease the production of growth hormone. These include:
- Kaʙergolin (Dostineks) – oral administration;
- Perholyd (Permaks) – oral administration;
- Bromocriptine (Parlodel) – It can be assigned to the operation,to reduce swelling;
- Octreotide (Sandostatin) – injectable (It may be the most effective drug for reducing the level of growth hormone);
- Pehvysomant – injectable, if other forms of treatment are not effective enough.
Prevention of acromegaly
Currently known steps to prevent acromegaly. Early treatment helps prevent serious complications.
