Congenital pulmonary valve insufficiency of the child
Description of congenital pulmonary valve insufficiency in a child
The absence of the pulmonary valve – a very rare heart disease.
In a healthy heart gets blood from the body into the right atrium, in right ventricle. Blood is pumped from the heart through the pulmonary artery into the lungs. It captures the fresh blood oxygen. Next, the blood returns to the left atrium of the heart and enters the left ventricle. There it is pumped through the aorta and delivering oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
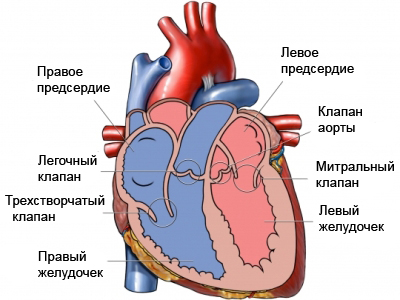
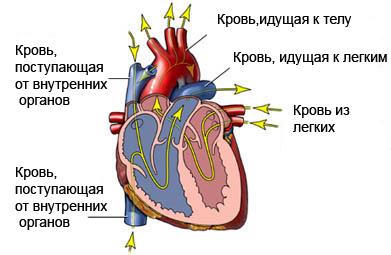
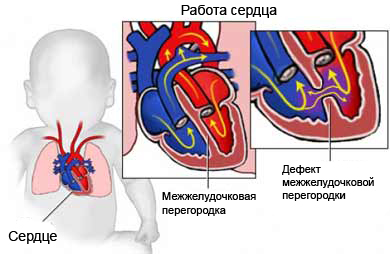
In the presence of this defect pulmonary valve is opened enough. This increases blood pressure, moving from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. Increased pressure causes swelling of these arteries, that can exert pressure on the airways in the lungs.
The disease can occur in various forms, Moderate to severe. It usually occurs with other heart diseases, as part of tetralogy of Fallot (group of heart defects), or with ventricular septal defect.
Causes of the disease
The absence of the pulmonary valve – congenital disease, vozniknveniya reasons which are not established yet.
Risk factors
Risk factors may include:
- Heredity;
- Chromosomal abnormalities;
- Previous pregnancy with abnormalities of the heart in the fetus or miscarriage.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Blue or pale grayish skin color;
- Breathing problems;
- Cough;
- Poor appetite / slow weight gain.
If your child has any of these symptoms, you need to see a doctor for help.
Diagnostics
For the diagnosis is necessary to pass the following tests:
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses sound waves, to see the size, form, and motion of the heart;
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses a small amount of radiation, to obtain images of the breast;
- Electrocardiogram - Analysis, which measures the electrical activity of the heart;
- MRI test – analysis, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the chest;
- CT scan – type of X-ray, which uses a computer, to obtain images of organs in the chest;
- Heart catheterization – analysis, that uses a catheter (tube) and x-ray machine to assess the condition of the heart and its blood supply.
Treatment
Treatment may include:
Surgical intervention
Surgery aims to restore the functioning of the blood flow. In simple cases, healing a ventricular septal defect may be sufficient. In other cases, you may need surgery to replace the valve. In this case, a synthetic valve, or human valve.
Condition Monitoring
After surgery, the child must be screened regularly by a cardiologist. Also, perhaps, require antibiotics and special procedures to prevent infection of the heart.
Prevention
Since the cause of the absence of the pulmonary valve is unclear, There is no way to prevent this disease.
